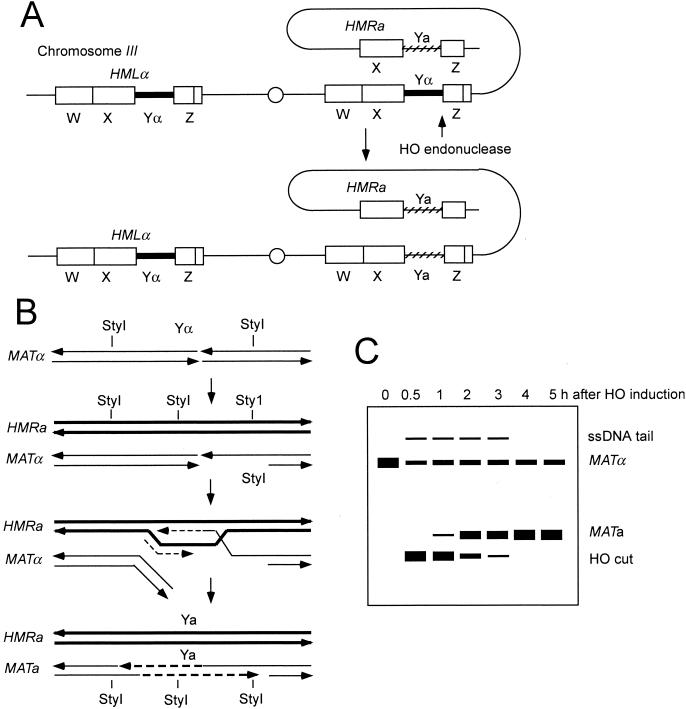
FIG. 5.
Mating-type switching. (A) Cartoon of chromosome III showing the silent cassettes, HMLα and HMRa and the expressed MATα locus. HO endonuclease cleaves between the Y and Z sequences, and repair using the HMRa donor results in switching to MATa. Regions of homology flanking Yα and Ya are indicated by W, X, and Z. (B) After HO cleavage, the 5′ end on the distal side of the break is resected and the resulting 3′ single-stranded tail invades the HMRa locus. DNA synthesis is primed from the invading strand, duplicating Ya sequences. Lagging-strand synthesis initiated from the D-loop results in synthesis of the other strand. The mechanism for removal of the Yα strands is currently unknown. (C) Schematic representation of a Southern blot showing the kinetics of mating-type switching. Switching to Ya results in transfer of a novel StyI site and therefore can be monitored by Southern blot analysis of DNA extracted after HO induction and digested with StyI. Resection of the 5′ strands beyond the distal StyI site results in resistance to digestion to StyI because the site is within ssDNA.