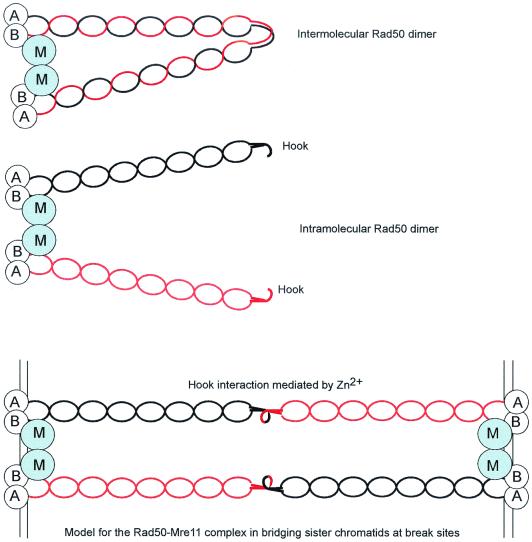
FIG. 9.
Models for the Rad50-Mre11 complex. A dimer of Rad50 could form by antiparallel intermolecular interaction to position the Walker A motif from one monomer next to the Walker B motif of the other. A dimer of Mre11 binds adjacent to the head-tail region of Rad50. Recent results are more consistent with an intramolecular interaction between the coiled-coil domains of Rad50, with the dimer held together by a dimer of Mre11. Interactions between the hinge domains could connect two dimers of Rad50 and two dimers of Mre11. The length of the Rad50 tetramer is consistent with the distance between sister chromatids in eukaryotes. The Mre11 and Rad50 head-tail domains are envisioned to interact with DNA.