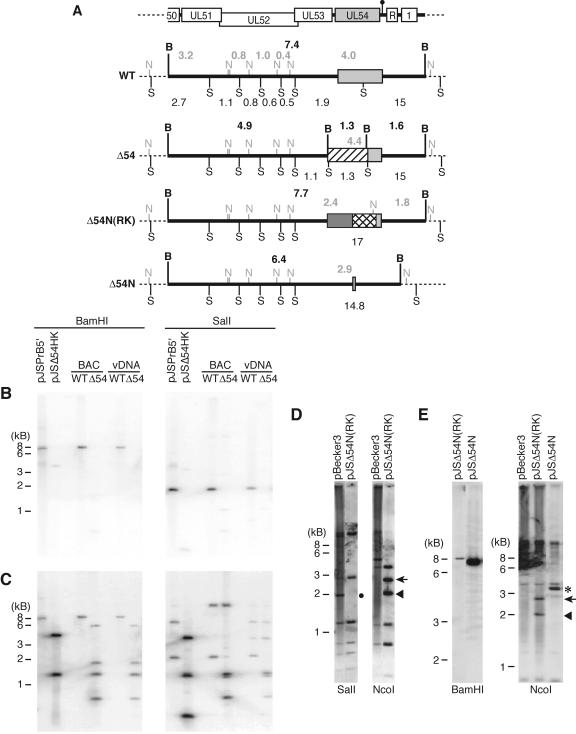
FIG. 2.
Southern blot analysis of the UL54 loci in BAC and virus DNAs. (A) Illustration of the restriction fragment length polymorphisms for BAC and virus DNAs from WT, Δ54 (pJSΔ54 and vJSΔ54), Δ54N(RK) [pJSΔ54N(RK)], and Δ54N (pJSΔ54N and vJSΔ54N). The top schematic diagram shows the relative positions of the genomic structures contained within the 5′ BamHI fragment (see the legend of Fig. 1 for key). Light gray boxes denote UL54 sequence. The thick black horizontal lines identify the 5′ BamHI fragment; sequence outside of this fragment is represented as a dotted line. The BamHI restriction sites (B) and the approximate fragment sizes (in kb; located above each diagram) are indicated in bold black type. The SalI restriction sites (S) and the relative fragment sizes (kb; located below each diagram) are identified by normal type, while the NcoI sites (N) and fragment sizes (kb) are represented in light gray type above each diagram. The Kanr, RpsL counterselectable, and neomycin selectable cassettes are shown as hatched, dark gray, or crosshatched boxes, respectively. (B to E) BAC and virus DNAs were digested with the indicated restriction enzymes and then electrophoresed through 0.8% agarose gels. The DNAs were depurinated and transferred to nylon membranes. The DNAs were hybridized to 32P-labeled (B and C) or biotinylated (D and E) DNA probes at 68°C. The membranes were washed and exposed to film (B and C) or developed using the NEB Phototope detection kit (D and E). Plasmid DNAs were used as controls. The plasmid pJSPrB5′ contains the 7.4-kb 5′ BamHI fragment from PRV, while pJSΔ54HK contains the H1 (Fig. 1)-targeted locus. The probes used were P5 (B), P6 (C), or P1 (D and E) (Fig. 1). The diagnostic 1.9-kb SalI fragment is highlighted by a black circle, while the diagnostic 1.8-, 2.4-, and 2.9-kb NcoI fragments are indicated by the arrowhead, arrow, and asterisk, respectively.