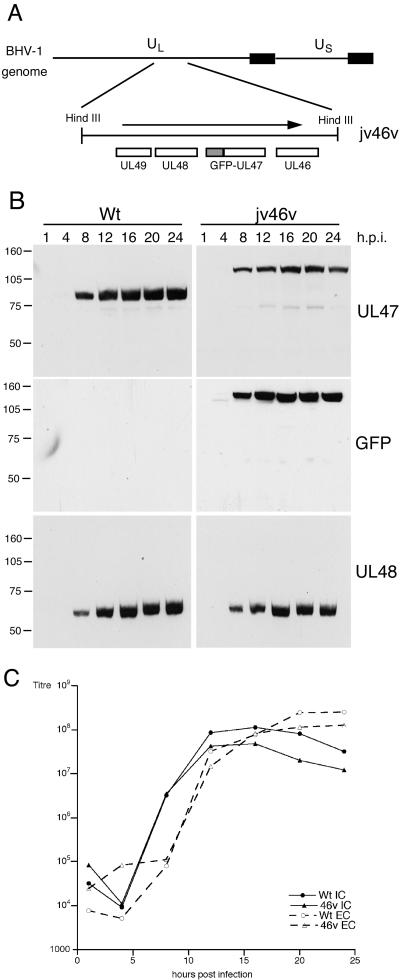
FIG. 1.
Insertion of GFP at the N terminus of UL47 has no effect on BHV-1 replication. (A) To construct a plasmid expressing GFP-UL47, the UL47 open reading frame was first transferred as a BamHI/XhoI fragment from plasmid pcVP8, in which the BamHI site is located seven bases upstream of the initiation codon (kindly provided by Vikram Misra, University of Saskatchewan) into pcDNAI/Amp. VP8 was then inserted into pEGFPC1 (Clontech) as a BamHI/XbaI fragment to create pJV2. Finally, 1 kb upstream of the VP8 gene was amplified by PCR from the BHV-1 genome (strain P8-2) as an AseI/AgeI fragment and inserted into AseI/AgeI-digested pJV2, resulting in plasmid pJV46 comprising GFP flanked by VP8 upstream sequences at the 5′ end and the VP8 gene at the 3′ end. Cotransfections were then carried out between pJV46 and infectious BHV-1 DNA, and resulting green fluorescent plaques were purified to generate recombinant virus jv46v. (B) MDBK cells infected with either wild-type BHV-1 (Wt) or the GFP-UL47-expressing virus (jv46v) at a multiplicity of 10 were harvested every 4 h up to 24 h after infection. Equal amounts of total cell extracts were analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies against UL47, GFP (Clontech), and UL48. (C) MDBK cells were infected with Wt or jv46v viruses at a multiplicity of 10 and were harvested every 4 h for both intracellular virus (IC) and extracellular virus (EC). Each sample was titrated on MDBK cells.