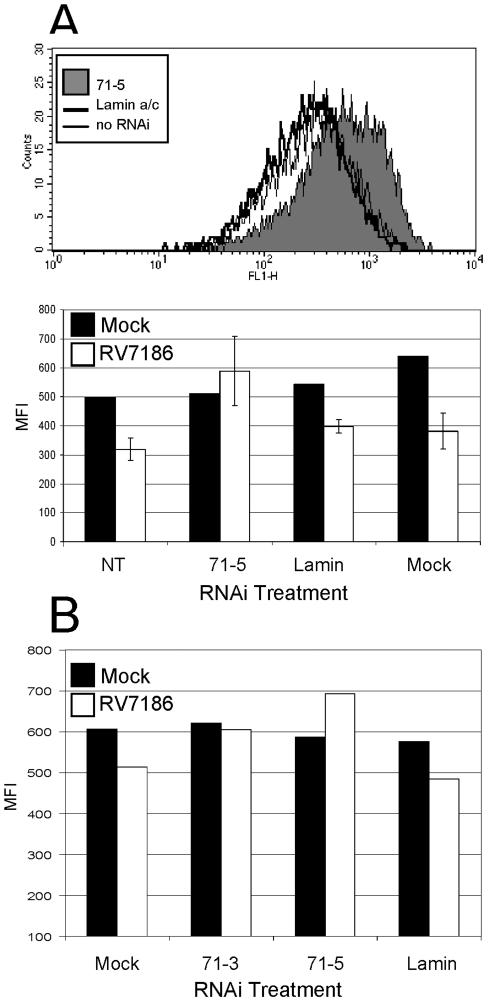
FIG. 10.
Knockdown of pp71 expression impacts MHC class I cell surface accumulation during infection. (A) Shown is a histogram and mean fluorescence intensities of MHC class I cell surface levels in RV7186-infected cells pretreated with RNAi duplexes. Cells cultured in 24-well plates were transfected with the indicated RNAi duplex. At 24 h after transfection, cells were mock infected or exposed to 3 PFU per cell of RV7186. Forty-eight hours after infection, cells were dislodged from the plates, reacted with FITC-conjugated anti-MHC class I antibody, and analyzed for cell surface MHC class I levels by flow cytometry. The upper panel shows representative histograms from of RV7186-infected cells pretreated with no RNAi, RNAi specific for lamin a/c, or RNAi specific for pp71. The lower panel shows the mean fluorescence intensities of mock-infected cells (averages of two replicate wells) and RV7186-infected cells (average of three triplicate wells) left untreated (NT) or transfected with RNAi duplexes specific for pp71 (71-3 or 71-5) or lamin a/c (lamin) or exposed to transfection reagent only (mock). (B) In a second experiment, triplicate wells of U373 cells in 24-well plates were mock infected or exposed to 10 PFU of RV7186 per cell 24 h after transfection with reagent only (mock) or RNAi duplexes specific for pp71 (71-3, 71-5) or lamin a/c. Cells from triplicate samples were dislodged from the plates, pooled, and analyzed for cell surface MHC class I levels by flow cytometry after reacting with FITC-conjugated anti-MHC class I antibody.