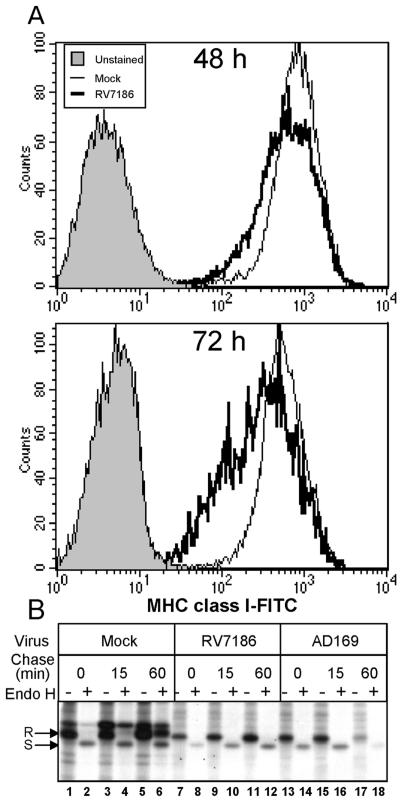
FIG. 8.
Delayed transport and cell surface accumulation of MHC class I complexes in RV7186-infected cells. (A) Histograms of MHC class I levels in mock- and RV7186-infected cells. U373:CIITA cells cultured in six-well plates were exposed to 2 PFU of RV7186 per cell or were left uninfected. Cells were dislodged from the plates at 48 and 72 h after infection, reacted with FITC-conjugated anti-MHC class I antibodies, and analyzed for cell surface MHC class I levels by flow cytometry. Histograms are shown for unstained cells, mock-infected cells, and RV7186-infected cells. (B) Autoradiographic image of MHC class I molecules from mock-, AD169-, and RV7186-infected cells with or without endoglycosidase H treatment. Triplicate cultures of U373:CIITA cells grown in 25-cm2 flasks were exposed to 2 PFU of the AD169 strain of CMV per cell or 2 PFU of mutant strain RV7186 per cell or were left uninfected. At 68 h after infection, cells were incubated with [35S]methionine for 30 min to radiolabel proteins. Cultures were washed with unlabeled media and further incubated for 0, 15, and 60 min after the pulse period. Cells were then solubilized, and MHC class I proteins were isolated with W6/32 anti-MHC class I antibody and protein A-agarose beads. One-half of the isolated proteins were incubated with endo H for 2 h as indicated in Materials and Methods. Proteins were separated in a 10% denaturing gel and visualized by autoradiography. Plus and minus signs indicate whether or not samples were treated with endo H. endo H-resistant and -sensitive forms of MHC class I molecules are denoted by R and S, respectively.