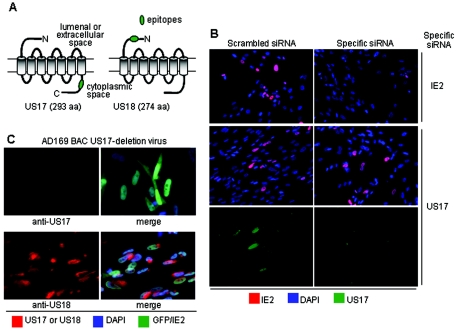
FIG. 1.
Generation and specificity of antibodies to US17 and US18. (A) Antipeptide antibodies were generated that target the indicated N-terminal and C-terminal domains of US18 and US17, respectively. aa, amino acids. (B) Use of siRNA to assess antibody specificity. IE-2 and US17 expression were inhibited by treatment with specific siRNAs (as indicated to the right). Cells in the scrambled siRNA column were treated with a nonspecific siRNA, which had no effect on IE-2 or US17 expression. IE-2 was stained red, nuclei were stained blue with DAPI, and US17 was stained green with a rabbit polyclonal antibody directed against the C-terminal segment. Nonconfocal images were obtained at ×20 magnification. (C) Lack of reactivity of US17 antiserum with cells infected with HCMV deleted for US17. HLF infected with an HCMV BAC recombinant from which the US17 gene was deleted were reacted with a monoclonal antibody against the IE-2 protein and rabbit antibodies against either US17 (top pair of panels) or US18 (bottom pair of panels). The BAC recombinant expresses GFP, so infected cells are dually positive for GFP and green fluorescence from the IE-2 staining. The anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G secondary antibody provided the red fluorescence. The right panels show green and red fluorescence merged, and the left panels show red fluorescence alone. Nonconfocal images were obtained at ×20 magnification.