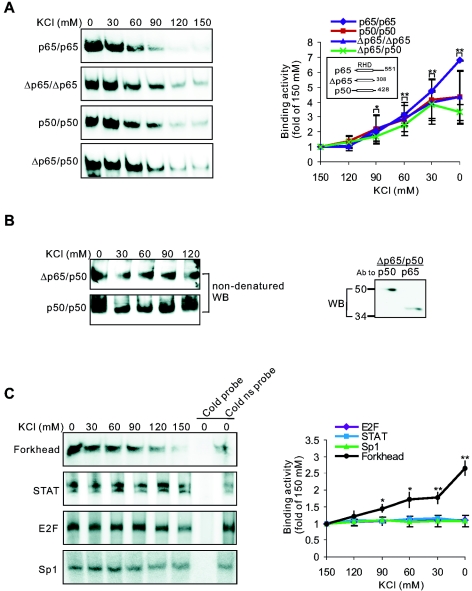
FIG. 8.
K+ directly and selectively affects the interaction between transcription factors and their DNA consensus sequences. (A) Effects of K+ on DNA-binding activities of recombinant NF-κBs were analyzed by EMSAs. (B) Effects of K+ on the dimerization of NF-κB subunits were analyzed with nondenatured Western blotting. Recombinant p50/p50 or Δp65/p50 was incubated with indicated K+ concentrations for 40 min at room temperature, and NF-κB complexes were then separated by a nondenatured 6% PAGE gel and Western blotted using antibody against p50. Denatured Western blot results (right) showed that both Δp65 and p50 were in the Δp65/p50 preparation. (C) Effects of K+ on DNA-binding activities of neuronal Forkhead transcription factor, STAT, E2F, and Sp1. ns, nonspecific. (A and C) Quantitative data represent means ± SEM of three to six independent experiments and are illustrated on the righthand panels. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 (versus 150 mM K+).