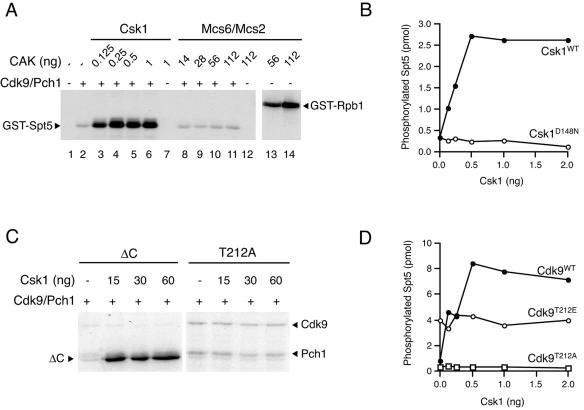
FIG. 2.
Activation of Cdk9/Pch1 by Csk1 in vitro. (A) Wild-type Cdk9/Pch1 complexes (150 ng per reaction) were preincubated with indicated amounts of purified Csk1 (lanes 3 to 6) or Mcs6/Mcs2 (lanes 8 to 11) plus cold ATP and tested for activity towards GST-Spt5(801-990). Activity of untreated Cdk9/Pch1 is shown in lane 2, and reaction mixtures lacking Cdk9/Pch1 but containing either Csk1 or Mcs6/Mcs2 were analyzed in lanes 7 and 12, respectively. The Mcs6/Mcs2 complex is active towards the Rpb1 CTD (lanes 13 and 14). The mobilities of radiolabeled GST-Spt5 and -Rpb1 polypeptides are indicated by arrowheads at the left and at the right, respectively. (B) Activity of wild-type Cdk9/Pch1 towards GST-Spt5(801-990) after preincubation with increasing amounts of wild-type or kinase-dead (D148N) Csk1 plotted as a function of the input Csk1 protein. (C) Csk1 phosphorylates Cdk9 in a manner dependent on Thr-212 in the T loop. The Cdk9/Pch1 complex (2 μg), Cdk9ΔC, or Cdk9T212A, as indicated above each panel, was incubated alone (first lane in each panel) or with increasing amounts (indicated at top) of wild-type Csk1 in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP. The electrophoretic mobility of the Cdk9ΔC polypeptide is indicated by the arrowhead at left, whereas the mobilities of radiolabeled full-length Cdk9 and Pch1 polypeptides are indicated by arrowheads at right. (D) Activation of Cdk9 by Csk1 is Thr-212 dependent. Activities of wild-type Cdk9, Cdk9T212A, and Cdk9T212E complexes towards GST-Spt5(801-990) after preincubation with increasing amounts of wild-type Csk1 are plotted as a function of the input Csk1 protein.