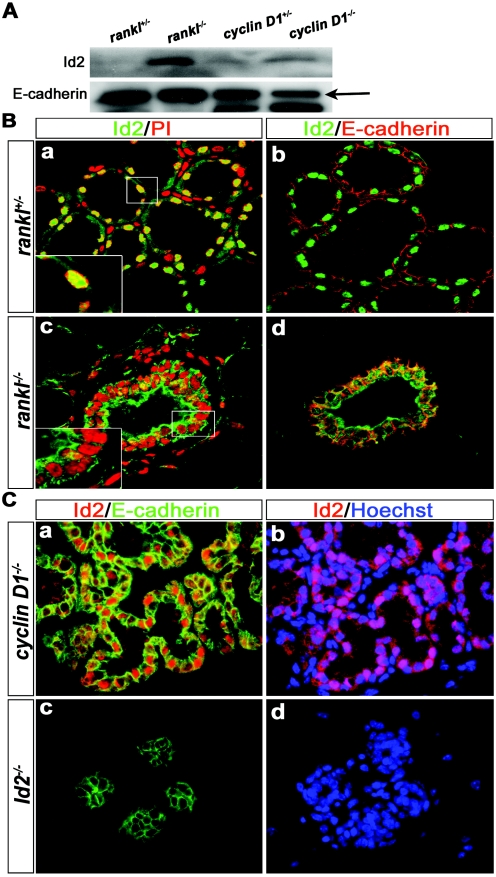
FIG.5.
Impaired nuclear translocation of Id2 in rankl−/− mammary glands. (A) Western blot analysis of Id2 in rankl+/−, rankl−/−, cyclin D1+/− and cyclin D1−/− mammary glands at L1. E-cadherin is shown as a protein loading control (black arrow). (B) Localization of Id2 in rankl+/− (upper panels) and rankl−/− (lower panels) mammary gland epithelial cells. Tissue sections of mammary glands from rankl+/− and rankl−/− mice at L1 were stained with anti-Id2 (a to d; green) and anti-E-cadherin (b and d; red) antibodies. Nuclear DNA was stained with PI (a and c; red). Images were acquired by using a confocal microscope (Leica Dmire2). Note the complete absence of Id2 in the nuclei of rankl−/− epithelial cells. Magnification, ×400. The magnified images are shown in the insets. (C) Tissue sections of mammary glands from cyclin D1−/− (upper panels) and Id2−/− (lower panels) mice at L1 were stained with anti-Id2 (a to d; red) and anti-E-cadherin (a and c; green) antibodies. Nuclear DNA was stained with Hoechst (b and d; blue). The specificity of antibody staining for Id2 was confirmed by its absence in Id2−/− mammary epithelium (c and d).