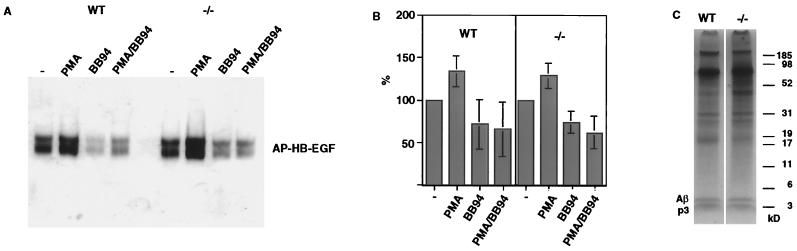
FIG. 4.
Shedding of HB-EGF and of APP in mdc9−/− cells. (A) Mouse embryonic fibroblasts were isolated from E13.5 wild-type or mdc9−/− embryos and transfected with HB-EGF-AP cDNA (see Materials and Methods). Cells were incubated with or without the phorbol ester PMA in the presence or absence of the hydroxamic acid-type metalloprotease inhibitor BB-94 for 1 h. The soluble ectodomain of HB-EGF-AP was precipitated with heparin-Sepharose, separated by SDS-PAGE, and renatured, and AP activity was visualized after incubating the gel in AP substrates (see Materials and Methods). (B) Bar graph of the results from eight separate experiments similar to the one shown in panel A, quantified using MacBas image analysis software. (C) Hippocampal neurons were isolated from E18.5 wild-type or mdc9−/− embryos. 35S-labeled APP and its degradation products p3 and Aβ were immunoprecipitated from cell supernatants and separated by SDS-PAGE. No difference in the level of p3 and Aβ released from wild-type and mdc9−/− hippocampal neurons was seen in three separate experiments.