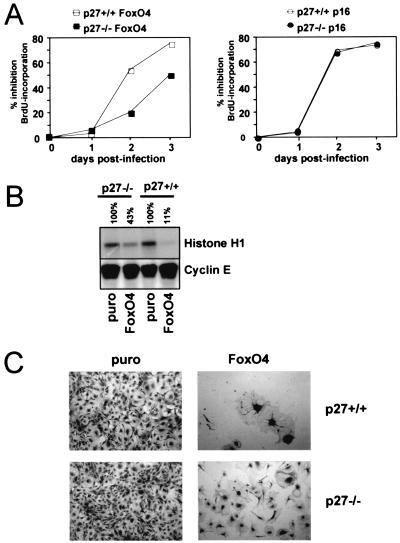
FIG. 1.
FoxO factor-induced cell cycle arrest does not depend on p27kip1 expression alone. MEFs from wild-type (p27+/+) or p27kip1-deficient (p27−/−) embryos were infected with an HA-FoxO4-containing retrovirus (FoxO4), a p16INK4a-containing retrovirus, or the parental retrovirus (puro) as indicated. (A) Time course of FoxO4-mediated (left panel) or p16-induced (right panel) DNA synthesis inhibition as determined by quantification of BrdU incorporation. Shown is the percent inhibition of BrdU incorporation compared to pBabe.puro-infected cells as a function of time. BrdU positivity of pBabe.puro-infected cells was around 50% at each time point, with no significant differences seen between the two genotypes (not shown). (B) Immunocomplex kinase assay for cyclin E-associated kinase using histone H1 as a substrate for immunoprecipitated cyclin E/CDK2 complexes. Lysates were taken 48 h postinfection. The percentage above each lane indicates the relative kinase activity compared to the control samples. Equal loading of immunoprecipitated cyclin E/CDK2 complexes was confirmed by Western blotting for cyclin E. (C) Light microscopic image showing morphology and densities of cells from the different infections after 10 days. A representative microscopic field is depicted. Each experiment was reproduced at least twice. Similar results were obtained with a retrovirus encoding a constitutively active FoxO3a mutant, HA-FoxO.A3 (data not shown).