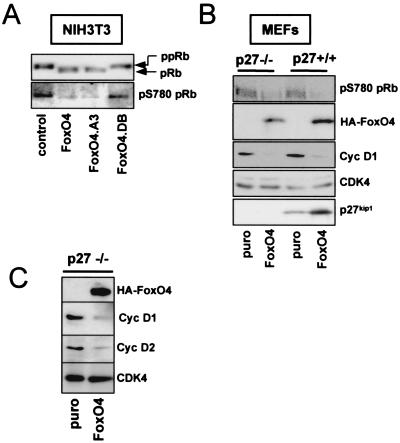
FIG. 2.
FoxO factor expression results in reduced protein levels of cyclins D1 and D2 and inhibits activity of cyclin D/CDK4 complexes in vivo. (A) NIH 3T3 cells were transiently transfected with an expression vector for Myc-tagged pRb in combination with either an empty control plasmid, a vector encoding full-length HA-FoxO4, or the indicated FoxO4 mutants, respectively. Forty-eight hours after transfection, exogenous Myc-pRb was immunoprecipitated from total lysates by using a monoclonal anti-Myc antibody, and CDK4-mediated phosphorylation of immunoprecipitated Myc-pRb was analyzed by Western blotting with a phosphospecific antibody against S780 (22). Similar loading of immunoprecipitated Myc-pRb was confirmed by staining the same blot with antiserum against total pRb. Phosphorylated pRb (ppRb) (upper band) migrates more slowly than unphosphorylated pRb (pRb) (lower band). (B) MEFs from wild-type (p27+/+) or p27kip1-deficient (p27−/−) embryos were infected with an HA-FoxO4-containing retrovirus (FoxO4) or a control retrovirus (puro). Forty-eight hours later, cells were harvested and total lysates were analyzed by Western blotting for the presence of HA-FoxO4, cyclin D1 (Cyc D1), or p27kip1. The cyclin D1 blot was additionally immunostained for CDK4 as a loading control. The activity of cyclin D/CDK4 complexes was judged by immunoblotting for phospho-S780pRb (pS780pRb). (C) Immortalized p27kip1−/− MEFs were infected as described for panel B and analyzed for protein expression of cyclin D1 (Cyc D1), cyclin D2 (Cyc D2), and HA-FoxO4 by Western blotting. CDK4 served as a loading control.