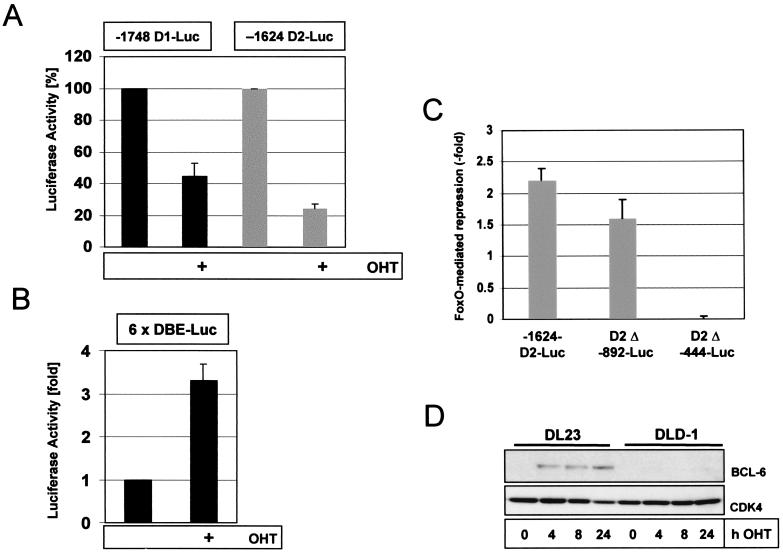
FIG. 6.
Conditional activation of FoxO3a decreases basal cyclin D1 and cyclin D2 promoter activities in human colon carcinoma cells. (A) Repression of cyclin D1 (−1748D1-luc) and cyclin D2 (−1624D2-luc) promoter activities by 4-OHT-induced FoxO3a activation (24 h). Luciferase values obtained with the untreated samples were set to 100%. (B) Confirmation of FoxO3a activation by 4-OHT using a forkhead-responsive luciferase plasmid containing six tandem repeats of DAF-16 binding elements (6×DBE-Luc) (12). (C) Effect of progressive deletion of cyclin D2-promoter sequences on FoxO3a.A3-mediated repression of cyclin D2-promoter-driven luciferase reporter activity in DLD1 colon carcinoma cells. Cells were transiently transfected with the indicated cyclin D2-luciferase reporter constructs (D2-luc) in combination with a FoxO3a.A3 expression vector or a control plasmid, and luciferase activity was assessed 48 h later. Depicted is the relative fold repression of luciferase activity by FoxO3a.A3 compared to control plasmid cotransfection. Graphs shown in panels A to C represent the average results from two independent experiments performed in duplicate, and error bars represent the standard error. (D) DL23 or DLD1 cells were stimulated with 100 nM 4-OHT and lysed at the indicated time points. Lysates were then analyzed for Bcl-6 expression by Western blotting. Levels of cyclin D2 and p27 in the lysates were examined in parallel, confirming the effectiveness of 4-OHT-mediated FoxO3a activation (Fig. 3B).