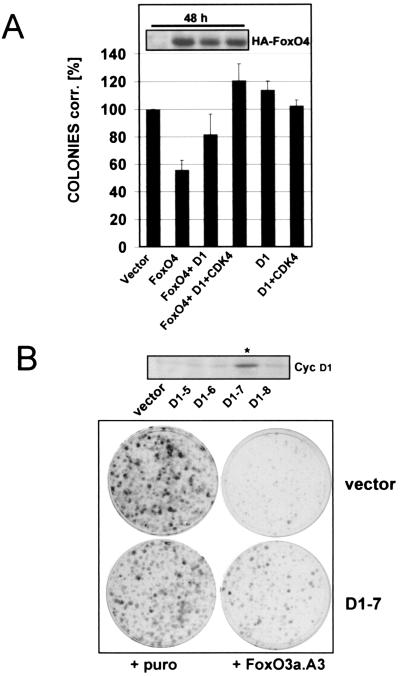
FIG. 8.
Exogenous cyclin D1 expression partially overcomes FoxO factor-induced cell cycle arrest. (A) Immortalized wild-type MEFs were transfected with pBabe.puro control vector (vector) or pBabe.puro-HA-FoxO4 (FoxO4) alone or in combination with cyclin D1 (D1) or cyclin D1/HA-CDK4 (D1/CDK4), respectively. Each combination was additionally cotransfected with limiting amounts of the fluorescent marker DsRed, and transfection rates were determined after 48 h by quantification of DsRed-positive cells by flow cytometry. Cells from each transfection were reseeded at equal dilutions into puromycin-containing selection medium, and colony formation assays were performed as detailed in Materials and Methods. Obtained colonies were counted, and numbers were corrected for transfection efficiency. Average values from two independent experiments are shown as percentages of corrected colonies + standard error. As a reference, values obtained with pBabe.puro empty vector were arbitrarily set to 100%. Western blot analysis of total lysates confirmed similar expression levels of ectopic HA-FoxO4 at the time point of reseeding (48 h after transfection [inset]). Similar results were obtained when experiments were alternatively performed with a different FoxO4 expression plasmid or when a retroviral construct expressing FoxO3a.A3 was used (data not shown). (B) Monoclonal immortalized wild-type MEFs stably expressing cyclin D1 (D1-7) or the corresponding polyclonal vector cell line (vector) were infected with empty pBabe.puro retrovirus or pBabe.puro encoding HA-FoxO3a.A3. The following day, cells from each infection were reseeded at equal numbers into selection medium and colony formation assays were performed as described in Materials and Methods. Crystal violet-stained colonies after 10 days of growth in selection medium are shown. The upper panel displays a Western blot for cyclin D1 demonstrating cyclin D1 overexpression of the selected D1-clone (indicated with an asterisk) compared to cyclin D expression of the negative clones and the utilized vector cell line.