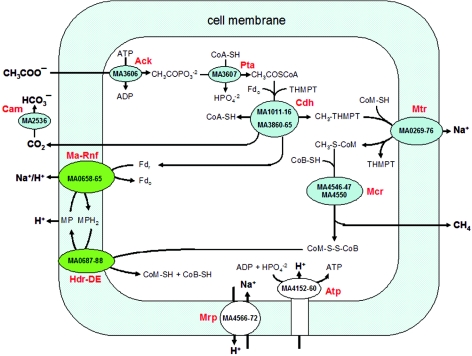
FIG. 1.
Pathway proposed for the conversion of acetate to methane by M. acetivorans. Ack, acetate kinase; Pta, phosphotransacetylase; CoA-SH, coenzyme A; THMPT, tetrahydromethanopterin; Fdr, reduced ferredoxin; Fdo, oxidized ferredoxin; Cdh, CO dehydrogenase/acetyl-CoA synthase; CoM-SH, coenzyme M; Mtr, methyl-THMPT:CoM-SH methyltransferase; CoB-SH, coenzyme B; Cam, carbonic anhydrase; Ma-Rnf, M. acetivorans Rnf; MP, methanophenazine; Hdr-DE, heterodisulfide reductase; Mrp, multiple resistance/pH regulation Na+/H+ antiporter; Atp, H+-transporting ATP synthase. Carbon transfer reactions are catalyzed by the enzymes shown in blue (see text). Electron transfer reactions are catalyzed by enzymes shown in green.