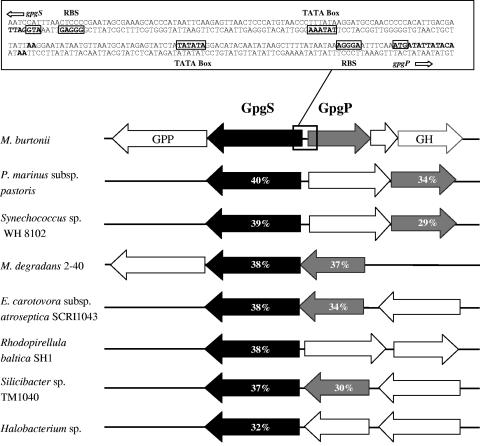
FIG. 1.
Genomic organization and flanking regions of gpgS and gpgP genes from M. burtonii (NCBI accession number for gpgS, ZP_00561711; accession number for gpgP, ZP_00561712) and their homologues in Prochlorococcus marinus subsp. pastoris MD4 (NP_893079 and NC_893077), Synechococcus sp. strain WH 8102 (NP_898525 and NP_898523), Microbulbifer degradans 2-40 (ZP_00317723 and ZP_00317722), Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica SCRI1043 (CAG75152 and CAG75151), Rhodopirellula baltica SH1 (CAD71863), Silicibacter sp. strain TM1040 (ZP_00620956 and ZP_00620955), and Halobacterium sp. (NP_279383). Arrows represent identified or putative GpgS proteins (black), identified or putative GpgP proteins (gray), and unknown open reading frames (open) and their orientations. The percentages of amino acid identity between homologous sequences are indicated inside the arrows. GPP, putative atypical UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase (ZP_00561714); GH, putative glucosyl hydrolase (ZP_00562149); RBS, ribosomal binding site.