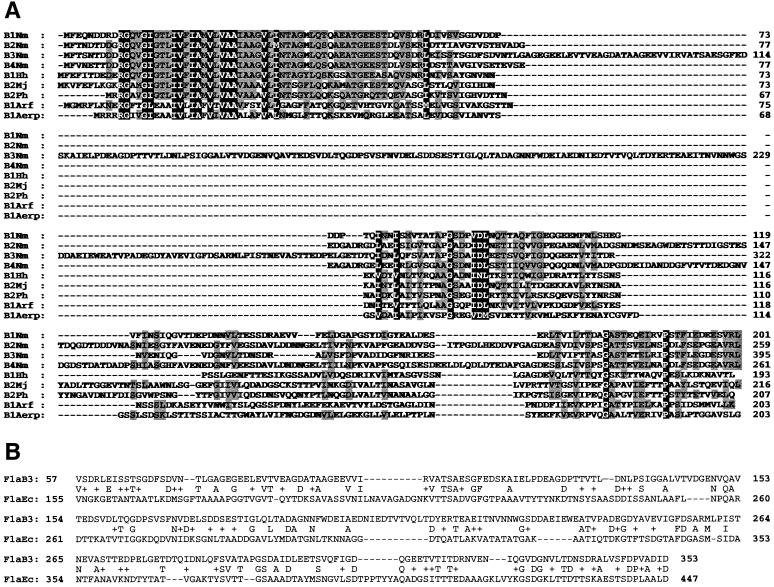
FIG. 2.
Homology between N. magadii and archaeal flagellins. (A) Multiple sequence alignment between N. magadii and representative archaeal flagellins was performed using ClustalW (39). Identical amino acids along with conserved substitutions were shaded with GeneDoc software (K. B. Nicholas and H. B. Nicholas, Jr., unpublished data). Amino acids similar in all proteins are white on a black background, and similar residues represented in >50% of the sequences are shaded in gray. The origins of the sequences were as follows: B1Nm to B4Nm, N. magadii; B1Hh, H. halobium (15); B2Mj, M. jannaschii (6); B2Ph, Pyrococcus horikoshii (22); B1Arf, Archaeoglobus fulgidus (24); B1Aerp, Aeropyrum pernix (23). (B) Comparison of the central parts of N. magadii FlaB3 and E. coli DEC 2a flagellins performed using BLAST (2).