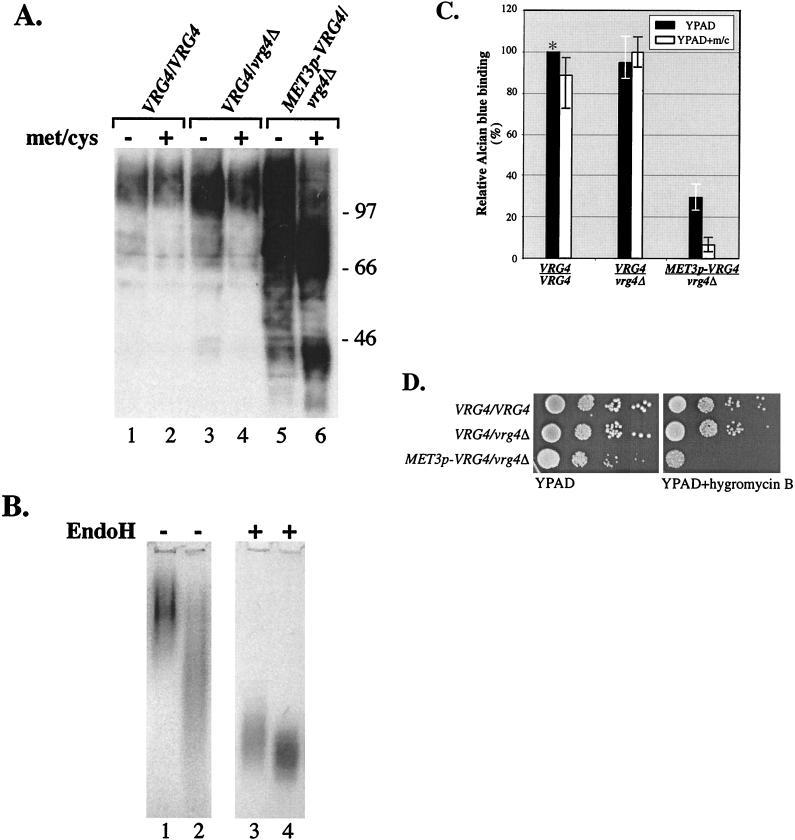
FIG. 6.
Loss of CaVRG4 function leads to mannosylation and cell wall-associated defects in C. albicans. (A) Proteins were isolated from wild-type strain BWP17, VRG4/vrg4Δ::hisG strain ANC2, and hemizygotic MET3p-VRG4/vrg4Δ::hisG strain ANC3 grown in YPAD with or without additional methionine and cysteine. After fractionation of equivalent amounts of protein by SDS-8% PAGE, mannoproteins were blotted with ConA-HRP and detected by chemiluminescence, as described in Materials and Methods. (B) Acid phosphatase in wild-type strain BWP17 (lanes 1 and 3) and vrg4 mutant ANC3 (lanes 2 and 4) assayed by native gel electrophoresis and visualized colormetrically (see Materials and Methods). Extracts were not treated or incubated with endo H prior to electrophoresis, as indicated at the top. (C) The strains used in the experiment whose results are shown in panel A were incubated with Alcian blue and subjected to dye binding assays (see Materials and Methods). Relative dye binding activity was calculated by determining the percentage of dye bound compared to the amount bound by the parental strain (BWP17) that had been grown in YPAD (see Materials and Methods). Each bar represents an average based on the results of four experiments. m/c, methionine and cysteine. (D) The strains used in the experiment whose results are shown in panel A were serially diluted and plated on YPAD or YPAD that was supplemented with 150 μg of hygromycin B per ml.