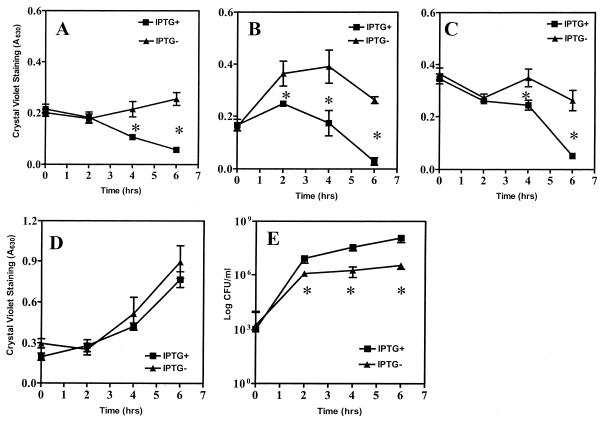
FIG. 6.
Dispersal of bacteria from preformed biofilm by csrA induction. A strain containing an IPTG-inducible csrA gene, TRJM101[pCSRH6-19], was allowed to form a 24-h biofilm, whereafter IPTG (1 mM final concentration) or sterile water (containing ampicillin in each case) was added directly to the medium (A), the medium was discarded and fresh CFA containing ampicillin with or without IPTG was added (B), the medium was replaced with a M63 salts solution containing ampicillin with or without IPTG (C), or 0.2% glucose and ampicillin with or without IPTG was added directly to the spent media (D). Biofilm remaining at the indicated times following csrA induction is shown. Each value represents an average of at least two independent experiments, with quadruplicate samples, and asterisks denote significant differences between induced and uninduced cultures (P < 0.0001). (E) The medium at 24 h was replaced with M63 salts solution containing ampicillin with or without IPTG (as for panel C), and planktonic cells that were released were recovered without disturbing the biofilm, were serially diluted, and were plated onto Kornberg medium. Plating efficiency (CFU/milliliter) was determined from two separate experiments, each including 3 countable plates (>30 but <300 colonies) for each time point. Each of the data points depicts the averages and standard errors of the two experiments; asterisks denote significant differences between the induced and uninduced cultures (P < 0.0001).