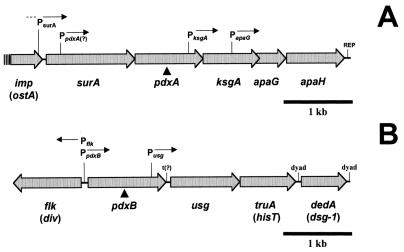
FIG. 1.
Structures of the pdxA and pdxB superoperons. (A) pdxA superoperon. The site of insertion of the pdxA::mini-MudI lacZ element in strain NU1187 (determined by restriction analysis) (55) is indicated by the solid triangle. The product of the imp gene is involved in organic solvent tolerance (1), and surA encodes a periplasmic peptidyl-prolyl isomerase that assists in the proper folding of outer membrane proteins (42, 57, 66). The likely position of the PsurA promoter is indicated (66). The probe for detection of pdxA-ksgA cotranscripts and ksgA-specific transcripts covers the region between the BglI and PvuII sites (see Materials and Methods) (55). (B) pdxB superoperon. The site of insertion of the pdxB::mini-MudII lacZ translational fusion element in NU1702 (solid triangle) was determined to be in frame by DNA sequencing (59). The probes for detection of pdxB and Pflk cover the region between the HindIII and TaqI sites (see Materials and Methods; 59).