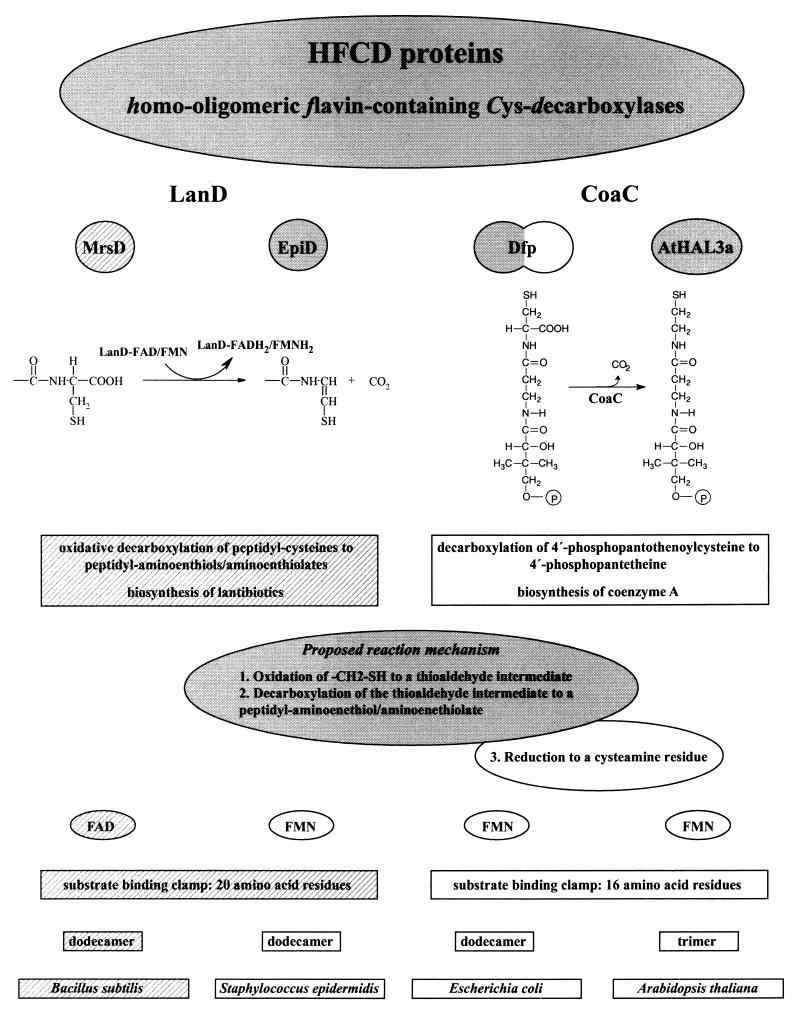
FIG. 7.
HFCD proteins with known enzymatic activity. The properties (from top to bottom: catalyzed reaction and proposed reaction mechanism, coenzyme requirement, structure of substrate binding clamp, oligomerization state, host organism) of the oxidative peptidyl-cysteine decarboxylases (LanD enzymes) MrsD (the present study), indicated by the hatched backgrounds, and EpiD (4, 20, 21, 23, 24) and the PPC decarboxylases (CoaC) Dfp (16, 24, 35, 37) and AtHAL3a (1, 11, 19) are compared in this figure. The proposed reaction mechanism for the LanD proteins is shaded in gray. The CoaC proteins reduce the oxidized intermediate to a cysteamine residue (reaction 3 of the proposed mechanism), so that in this case the overall reaction is a decarboxylation and not an oxidative decarboxylation. The length of the substrate binding clamp of MrsD is taken from the structure-based alignment of EpiD with MrsD (4). Dfp has PPC decarboxylase (NH2-terminal domain shaded in gray) and PPC synthetase activity (COOH-terminal domain).