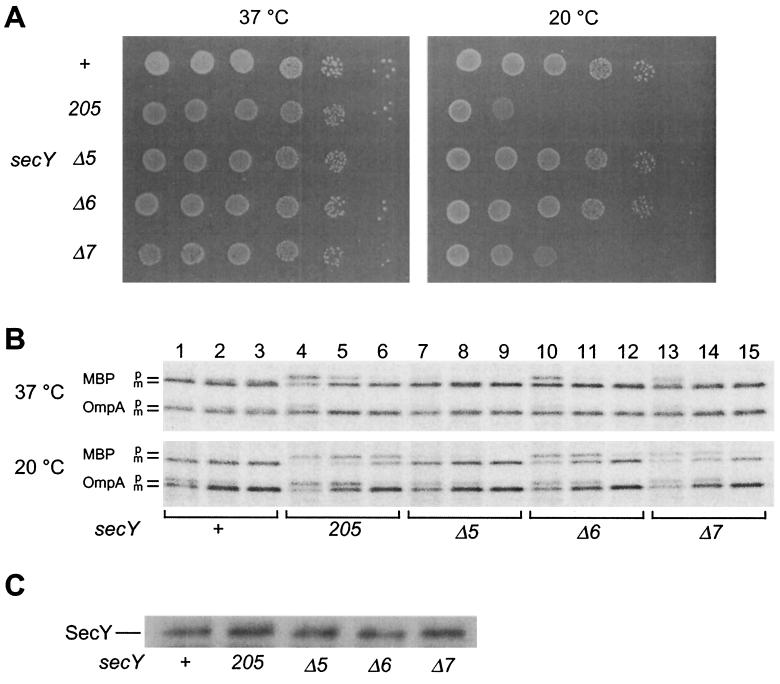
FIG. 1.
Growth and protein export phenotypes of chromosomal secY mutants. (A) Growth at 37 and 20°C. Strains TW156 (secY+), GN5 (secY205), KC5 (secYΔ5), KC6 (secYΔ6), and KC7 (secYΔ7) were cultured at 37°C until mid-log phase. Cells were serially diluted with 0.9% NaCl solution (10-fold dilutions from left to right), and 2 μl of each was spotted on L-agar plates, which were photographed after 12 h at 37°C (left panel) or after 48 h at 20°C (right panel). (B) Protein export phenotypes. Cells were grown at 37°C (upper panel) and then at 20°C for 30 min (lower panel), followed by pulse-labeling with [35S]methionine for 30 s at 37°C or for 1 min at 20°C and chase with unlabeled methionine for 12 s (lanes 1, 4, 7, 10, and 13), 1 min (lanes 2, 5, 8, 11, and 14), and 5 min (lanes 3, 6, 9, 12, and 15). MBP and OmpA were immunoprecipitated and subjected to SDS-PAGE and phosphor imager visualization. (C) Cellular accumulation of the mutant SecY proteins. Whole-cell proteins from a fixed number of cells of mid-log-phase M9 cultures were subjected to SDS-PAGE and anti-SecY immunoblotting.