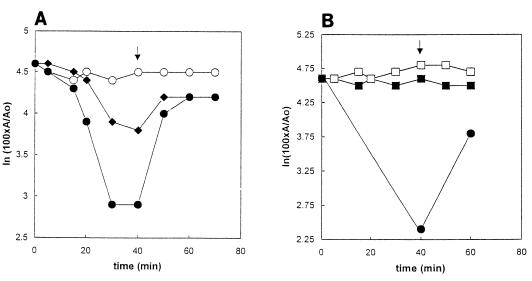
FIG. 9.
Effect of DEPC and subsequent addition of hydroxylamine hydrochloride on HMG-CoA reductase activity. (A) Effect on reaction 3, the reductive deacylation of HMG-CoA to mevalonate. Treatment with DEPC and with hydroxylamine hydrochloride was conduced on ice. Samples contained fusion protein in a solution containing 250 mM KCl, 10% (vol/vol) glycerol, 250 mM K xPO4, pH 6.5. DEPC in ethanol was added to a concentration of 0.8 (⧫) or 8.0 mM (•). A control contained ethanol but no DEPC (○). After 40 min, hydroxylamine hydrochloride, pH 6.5, was added to a concentration of 700 mM (arrow). Ten-microliter portions removed at the indicated times were assayed for the ability to catalyze reaction 3, the reductive deacylation of HMG-CoA to mevalonate. Ao and A are the specific activities at zero time and at the indicated times, respectively. (B) Effect on reaction 4, the reductive deacylation of mevaldehyde to mevalonate. Reaction conditions were as described above but at pH 7.0 and using 8 mM DEPC and an ethanol control (□). Data for reaction 4 (▪) are shown. Also shown are data for reaction 3 (•), included to establish that reaction with DEPC had indeed occurred.