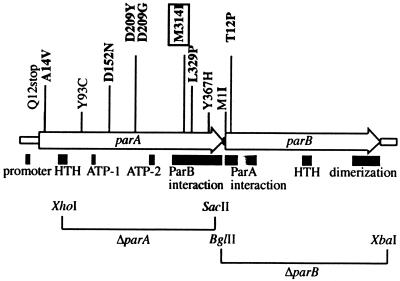
FIG. 2.
P1 par operon map. The mutations are shown above the map. Names correspond to the amino acid change and position. Thus, parAA14V has an alanine-to-valine change at the 14th ParA amino acid. Mutations in bold type are those that impose a transcription block in the test strain (Fig. 1). Those in regular type relieve the transcription block imposed by the previously isolated mutation, parAM314I (boxed). Features of the Par region are indicated as boxes below the map. HTH, helix-turn-helix motif probably involved in binding to the par operator sequence (ParA) or the parS site (ParB); ATP-1,2, first and second ATPase motifs. The regions implicated in the ParA-ParB interaction are also shown (23), as is the ParB dimerization domain (27).