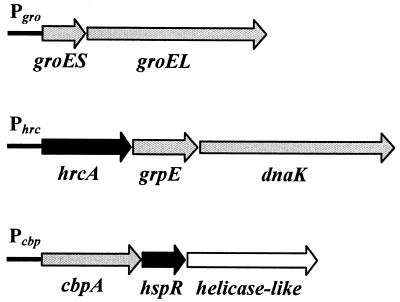
FIG. 1.
Structural organization of H. pylori chaperone genes (17, 21). Grey arrow bars indicate chaperone genes, black arrow bars indicate regulatory genes (hspR and hrcA), and the white arrow bar indicates a putative helicase-like gene. Chaperone genes groES and groEL code for the HspA (Hsp10) and HspB (Hsp60) proteins (20); cbpA encodes a protein with 30% amino acid identity (in a 288-amino-acid overlap) to the cochaperone curved DNA binding protein CbpA from E. coli, a homologue of DnaJ (22); hspR encodes a regulatory protein with 46% identity (in a 91-amino-acid overlap) to HspR, the negative regulator of heat shock genes in S. coelicolor (2); the helicase-like open reading frame encodes a protein with 30% identity within 421 amino acids to a hypothetical helicase-like protein from Haemophilus influenzae; hrcA encodes a protein with 28% identity (in a 71-amino-acid overlap) to the heat-inducible transcriptional repressor HrcA from B. subtilis (23); and grpE and dnaK encode the GrpE and DnaK (Hsp70) chaperones, respectively.