Figure 1.
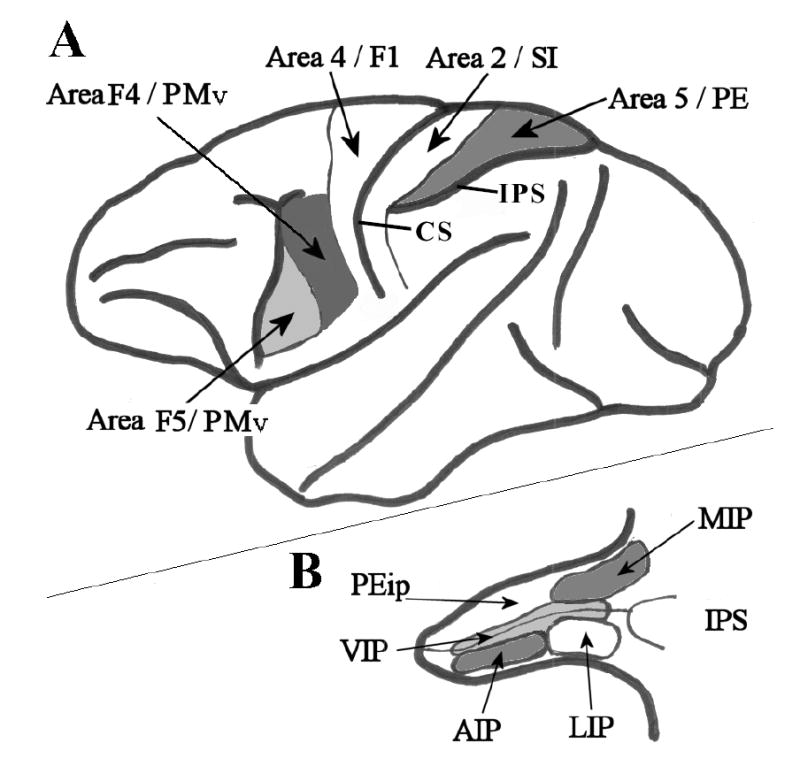
Selected cortical areas of the Macaque monkey brain. A. Lateral view of the whole brain. Thick black lines represent major cortical boundaries and sulci. Thin black lines represent cortical area boundaries. Area 4/F1 - primary motor cortex; Area 2/SI – primary somatosensory cortex; Area 5/PE – posterior parietal association cortex/superior parietal lobule; Area F5/PMv – where ‘mirror neurons’ were first recorded. Area F4/PMv – ventral premotor cortex. IPS – intraparietal sulcus; CS – central sulcus. B. The intraparietal sulcus has been opened up to reveal multiple and heterogeneous visual and somatosensory posterior parietal areas. Thick lines represent the superficial border of the sulcus; thin black lines mark the fundus of the sulcus. Other lines indicate the boundaries of cortical areas as follows: MIP – medial intraparietal sulcus; LIP – lateral intraparietal sulcus; AIP – anterior intraparietal sulcus; VIP –ventral intraparietal sulcus; PEip – intraparietal portion of area PE. (Redrawn from Rizzolatti et al., 1998).
