Figure 4.
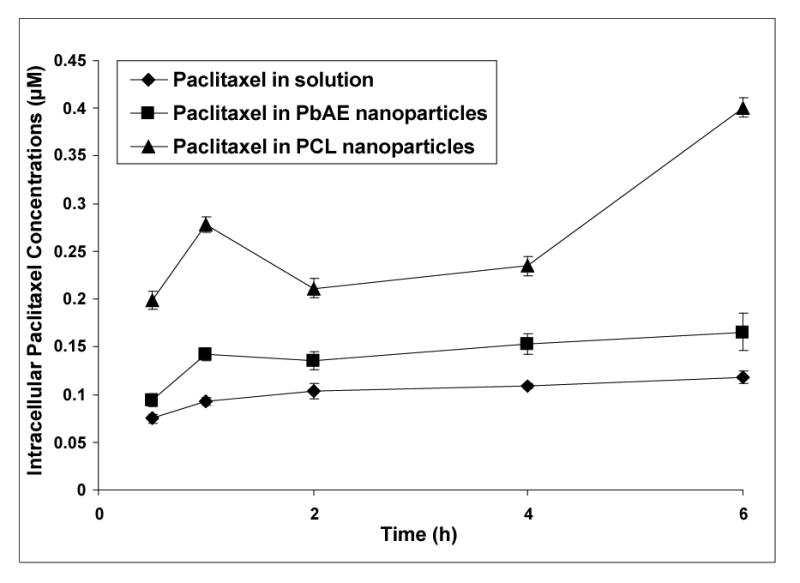
Intracellular paclitaxel concentrations upon continuous exposure of the drug in different formulations. Comparison between aqueous solution formulation, poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO)-modified poly(β-amino ester) (PbAE) nanoparticles, and PEO-modified poly(ɛ-caprolactone) (PCL) nanoparticles. For studying quantitative uptake of nanoparticles containing [3H]-paclitaxel, MDA-MB-231 human breast adenocarcinoma cells were seeded into 12-well plates (approx. 10,000 cells per well) and allowed to adhere by overnight incubation at 37°C. The growth medium was replaced with serum-free media and the formulations were added as an aqueous solution or as nanoparticle suspensions in sterile phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4). For continuous exposure studies, the plates were incubated and at periodic time intervals, the cells were washed with sterile PBS and digested with 1% w/v Triton® X-100 solution. Radioactivity levels in the cell lysates was determined using a liquid scintillation counter and the values were converted into micromolar concentrations of paclitaxel normalized to protein content per well.
