Figure 6.
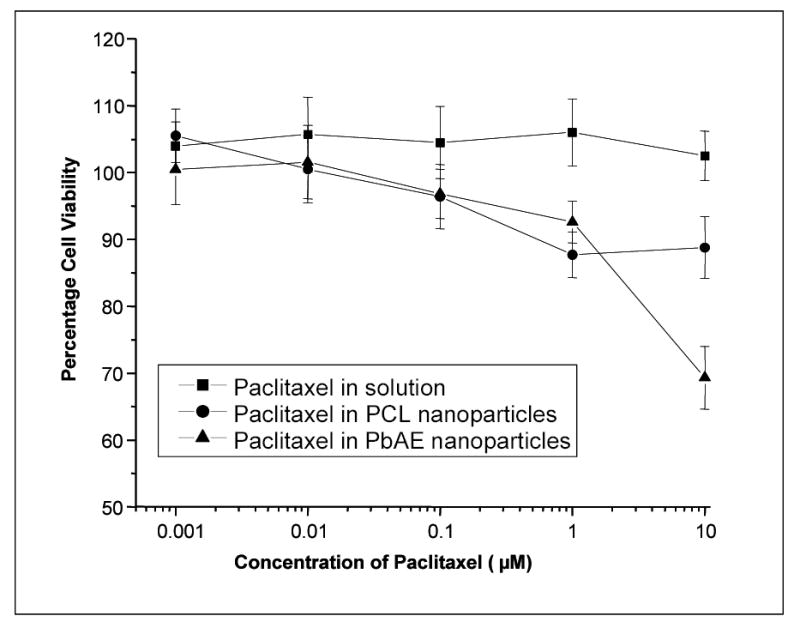
Percentage cell viability as a function of paclitaxel concentrations delivered in various formulations. Comparison between aqueous solution formulation, poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO)-modified poly(β-amino ester) (PbAE) nanoparticles, and PEO-modified poly(ɛ-caprolactone) (PCL) nanoparticles. MDA-MB-231 human breast adenocarcinoma cells, seeded in 96-well plates, at a density of approximately 5,000 cells per well, were allowed to adhere overnight at 37°C. The growth medium was replaced with serum-free media (SFM) and the graded concentrations of paclitaxel, either as an aqueous solution or as nanoparticle suspension, were added to the wells. After 6 hours of incubation, SFM was replaced with a mixture of growth media (DMEM) and (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium, inner salt (MTS), and incubated for an additional 4 hours. Absorbance of the control and the treated cells were read at 492 nm using a microplate reader and percentage cell viability values were calculated relative to the untreated control.
