Fig. 2. Mapping Bcl-2 homodimerization interface using site-specific photocross-linking.
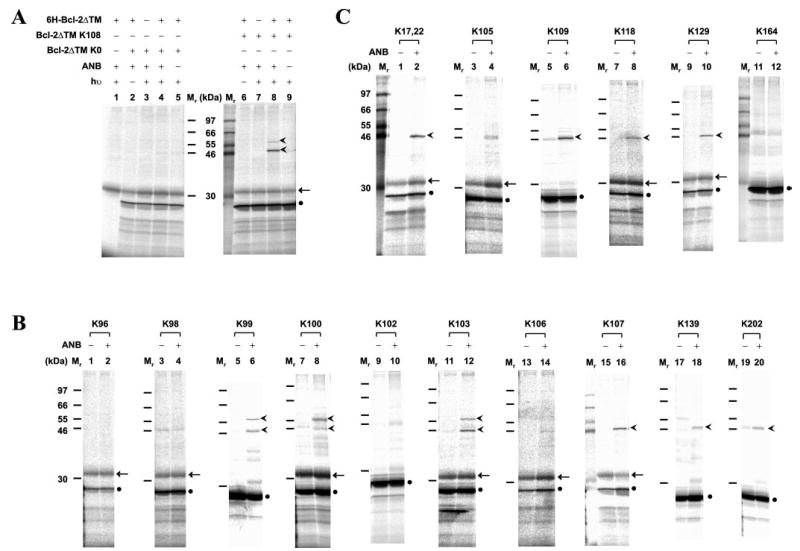
A, photocross-linking of in vitro synthesized Bcl-2ΔTM with a single ANB probe attached to Lys108 to His-tagged Bcl-2ΔTM. After cross-linking, the fraction that bound to Ni2+-chelating resin was eluted, and photoadducts were separated by SDS-PAGE and detected by phosphorimaging (indicated by the arrowheads adjacent to lane 8). The adducts were not detected in control reactions lacking RNA encoding of Bcl-2ΔTM K108, UV irradiation (hν), 6H-Bcl-2ΔTM protein, or εANB-Lys-tRNALys (ANB), as shown in lanes 1, 6, 7, and 9, respectively. The adducts were also absent when RNA encoding Bcl-2ΔTM K0 was used (lanes 2–5). Background detected in some or all of the control reactions included in vitro synthesized Bcl-2ΔTM and an unidentified reticulocyte protein, indicated by a filled circle and arrow, respectively. The Mr of standards is indicated between the two panels. B and C, photocross-linking of His-tagged Bcl-2ΔTM proteins to in vitro synthesized Bcl-2ΔTM mutant proteins, each with a single ANB probe attached to a Lys residue within the acceptor surface or the donor surface, respectively (defined in Fig. 3). The symbols used to indicate Bcl-2ΔTM photoadducts, background proteins and Mr of standards are defined in A.
