Fig. 2.
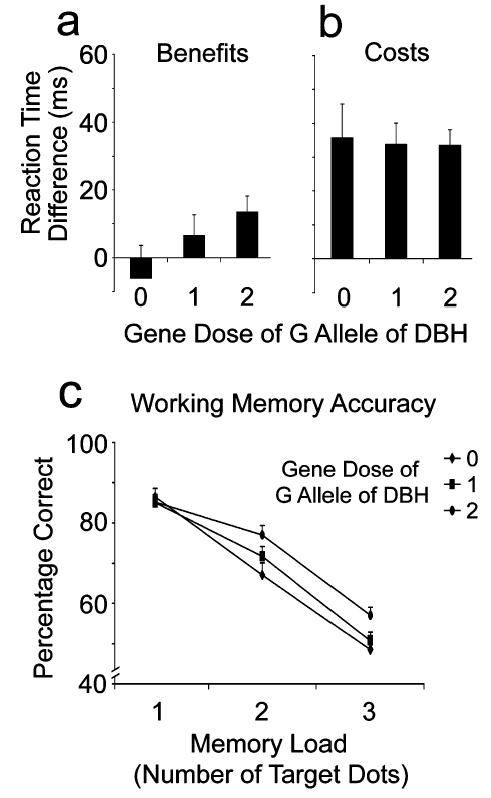
Effects of allelic variation in the dopamine beta-hydroxylase (DBH) gene on visuospatial attention in the 2,000-ms stimulus-onset asynchrony condition and on working memory: (a) reaction time (RT) benefits of valid location cues in the visuospatial attention task (neutral RT – valid RT), (b) RT costs of invalid location cues in the same task (invalid RT – neutral RT), and (c) match accuracy in the working memory task as a function of number of spatial locations to be maintained in working memory. The three genotypes AA, AG, and GG correspond to increasing gene dose (0, 1, 2) of the G allele of the DBH gene.
