Figure 1.
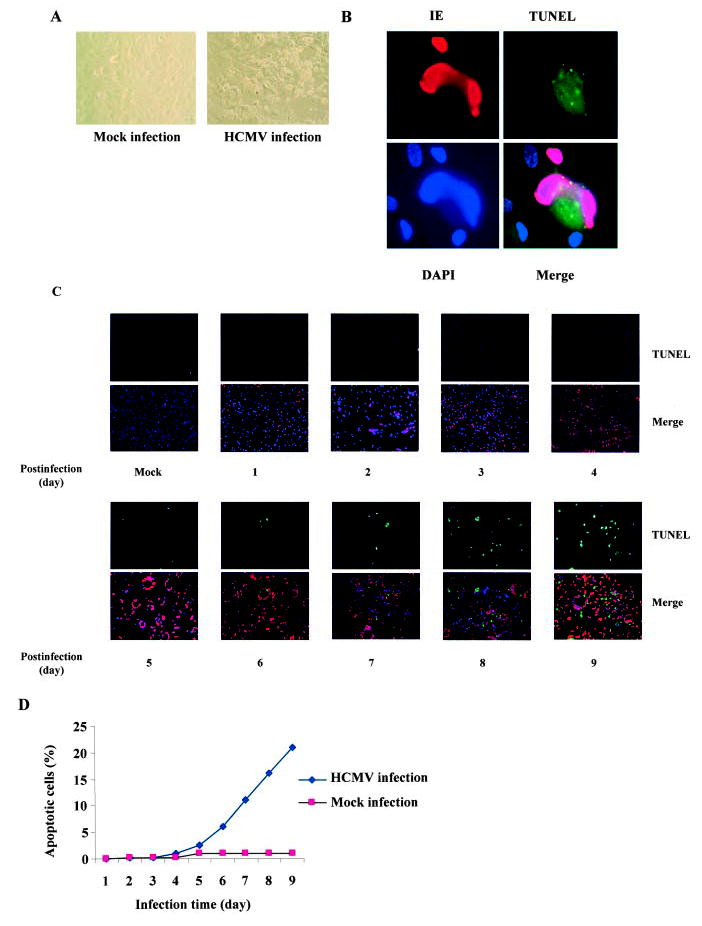
Prolonged HCMV infection induced endothelial apoptosis. A, HCMV infection resulted in substantial cytopathicity in endothelial cells. HAECs were infected with VHL/E strain of HCMV for 9 days and changes in morphology and viability were observed under light microscope. B, Detection of endothelial apoptosis in HCMV-infected HAECs. VHL/E-infected HAECs (day 9 pi) were stained with anti-IE (HCMV immediate early antigen) antibody to indicate infected cells (red), TUNEL (green) for apoptosis, and DAPI (blue) for nuclei. Merged image shows colocalization. C, Time-dependent apoptosis of HCMV-infected HAECs. HAECs were infected with VHL/E for indicated time periods; cells were stained with anti-IE antibody (red), TUNEL (green), and DAPI (blue). Merged images show colocalization. D, Time-dependent death curves of VHL/E-infected HAECs. TUNEL-positive cells and total cells were counted in 5 fields per coverslip. Results were expressed as the average percentage of TUNEL-positive cells over total cells.
