Figure 1. Expression of an NR2B subunit with a mutation at Y1472 causes a specific increase in NMDA-mEPSC amplitude.
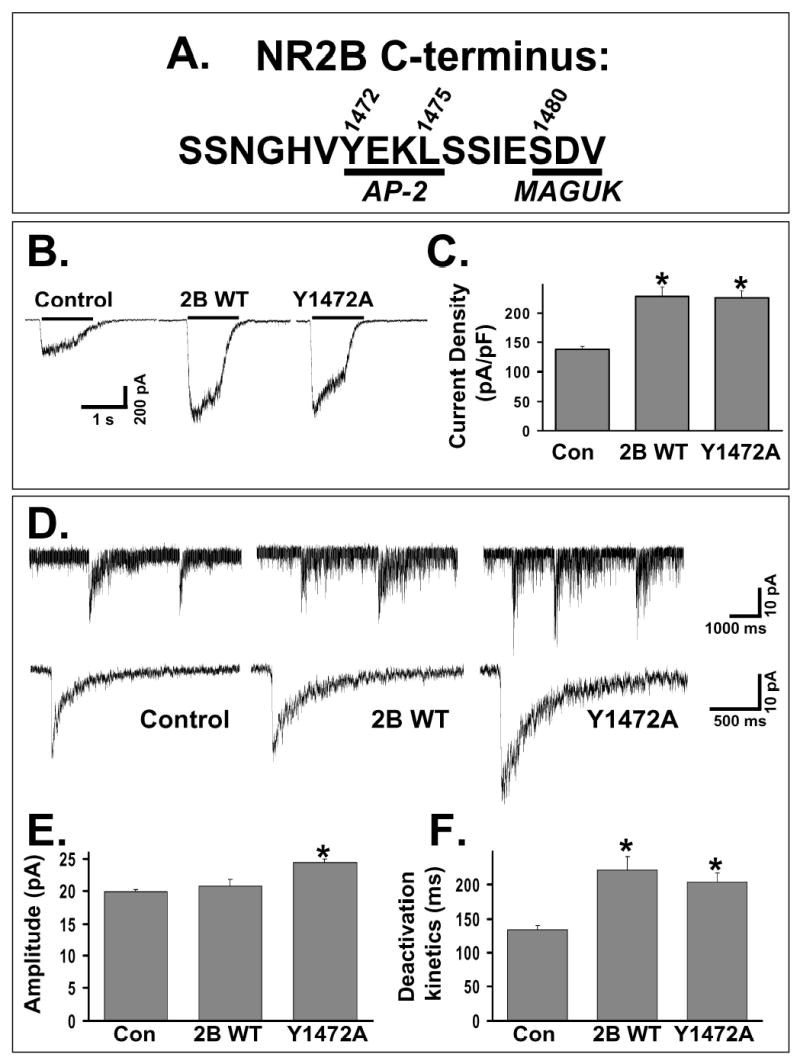
A: The amino acid sequence of the distal C-terminus of the NR2B subunit. Two motifs are underlined, a consensus internalization motif for AP-2 binding (YEKL, 1472-1475) and the PDZ-binding domain that mediates MAGUK binding (SDV, 1480-1482). Amino acids 1472, 1475, and 1480 are sites where mutations were made.
B: Representative traces from control CGC or CGC transfected with cDNAs for wildtype or mutant subunits of the NMDAR. Whole-cell recordings were done 48 hours after transfection with application of 200 μM NMDA and 20 μM D-serine with 1 μM TTX in Mg2+-free solution.
C: Summary of current density responses from multiple CGCs (control, n = 10; NR2B WT, n = 12; Y1472A, n= 15). Transfection with either NR2B WT or Y1472A caused a similar, significant increase in the current density of response (p < 0.01, ANOVA).
D: Representative NMDA-mEPSCs recorded and averaged from individual control or transfected (with NR2B WT or Y1472A) CGCs. Recordings were made in Mg2+-free extracellular solution with 50 μM bicuculline, 1 μM TTX, and 10 μM NBQX.
E: Average amplitude of NMDA-mEPSCs from multiple CGCs (control, n = 25; NR2B WT, n = 15; Y1472A, n= 20). Expression of NR2B WT caused no change in amplitude compared to untransfected CGCs, but expression of Y1472A caused a significant increase (ANOVA, * = p<0.01).
F: Average of the weighted time constant of decay (τw) from multiple CGCs. Expression of either NR2B WT or Y1472A caused a significant slowing of the deactivation kinetics of the NMDA-mEPSCs (ANOVA, * = p<0.01).
