Fig. 2.
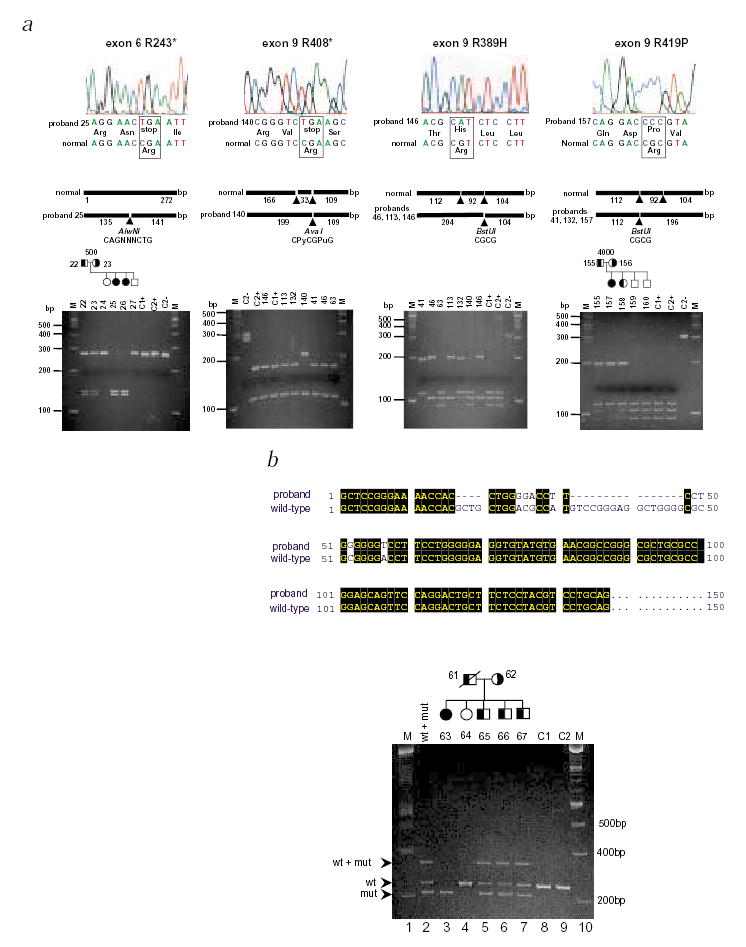
Mutational analyses in ABCG5 in sitosterolemia probands. a, The top panels show the sequence electropherograms; the middle panels, the sizes and restriction enzyme fragments; and the bottom panels, the gel electrophoresis of digested PCR fragments. Mutation R243X (left-hand panels) results in a gain of the AlwnI site. Using this as an assay, this mutation segregated within pedigree 500. Similarly, mutation R419P causes a loss of the second BstUI site and can be shown to segregate appropriately in pedigree 4000 (right-hand panels). BstUI can also be used to screen for R419H (data not shown). Additionally, the first BstUI site is altered by mutation R389H (middle right panels). Thus, digestion of the exon 9 PCR product with BstUI allows screening of all three mutations. Mutation R408X alters AvaI site (middle left panels). Control samples are indicated by the letters C1 and C2, with + or – indicating digested and undigested samples. Marker tracks (M) are as indicated. b, Following the detection of an abnormal SSCP for exon 3, direct sequencing of the PCR product revealed complex deletion and base substitutions, as depicted by the CLUSTALW alignment of the mutant product with the wild-type sequence. After re-designing the primer-pairs (exon3F and exon3R) to better detect the 20-bp size difference, the mutant alleles could be shown to segregate within pedigree 2100. Lane 2 contains a mixture of wild-type and mutant PCR products that were mixed, denatured and annealed before loading. The slower migrating band is therefore a hybrid between a wild-type strand and a mutant strand. Its presence is detected in heterozygotes only (lanes 5, 6 and 7). Based upon haplotype analyses, siblings 65, 66 and 67 are predicted to be carriers and sibling 64 is homozygous wild type, in good agreement with the segregation of the deletion. Maternal non-paternity was detected in this family and her sample was excluded from analyses (data not shown).
