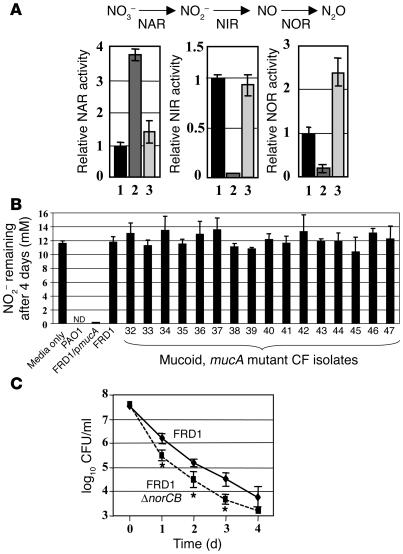
Figure 5.
Significantly reduced NIR and NOR activities in mucA mutant P. aeruginosa account for the sensitivity to HNO2. (A) Relative activities of NAR, NIR, and NOR in FRD1 (lane 2) and FRD1/pmucA (lane 3), normalized to that of the well-characterized laboratory strain PAO1 (lane 1). Each assay was performed in triplicate, and the mean ± SEM is presented. A schematic diagram of the P. aeruginosa anaerobic respiration pathway is shown. Bacteria were grown in LB (pH 6.5) containing 100 mM NO3– for 15 hours under anaerobic conditions. (B) P. aeruginosa strains were incubated anaerobically in LB containing 15 mM NO2–, pH 6.5. After 4 days at 37°C, NO2– levels were measured in triplicate. All other mucA mutant clinical isolates were among those described in Supplemental Table 1. For the media-only control, no bacteria were used. ND, not detected. (C) Anaerobic sensitivity of FRD1 and FRD1 norCB mutant exposed to NO2– at pH 6.5. Experimental conditions were identical to those used in Figure 2B. Δ, deletion of a specific gene. *P < 0.01 versus FRD1.