Fig. 6.
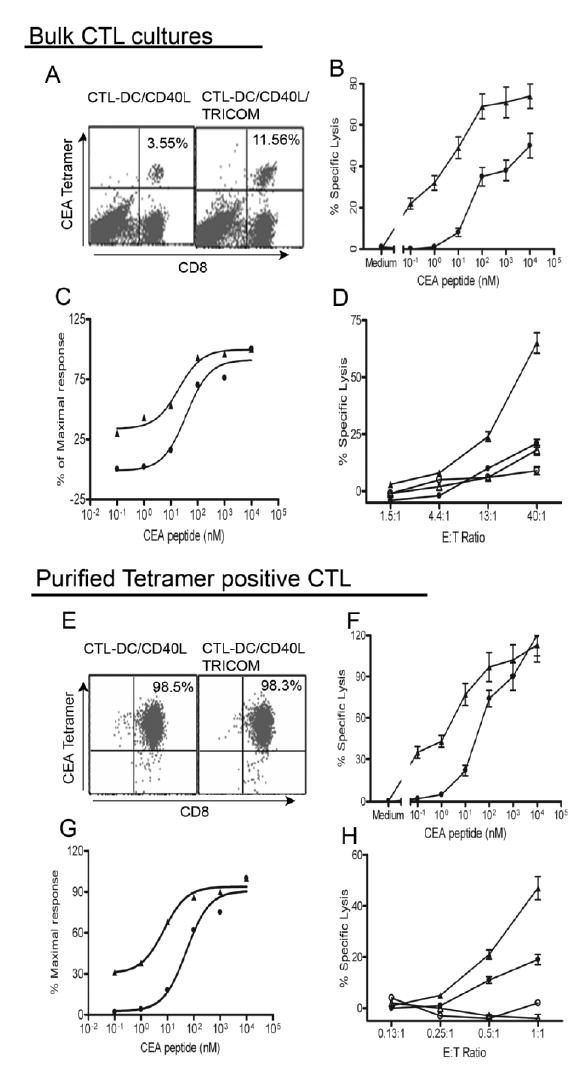
CTL elicited by peptide-pulsed, CD40L-matured DC infected with rF-TRICOM more efficiently lyse tumor cells presenting endogenously processed CEA antigen. DC were generated with GM-CSF/IL-4 for 6 days and matured with CD40L for 24 hours. CD40L-matured DC were infected with either FP-WT (closed circles) or rF-TRICOM (closed triangles) and then loaded with CEA peptide for induction of peptide-specific CTL from autologous Pan T cells. After three cycles of in vitro stimulation (IVS), bulk cultures were analyzed for tetramer staining, avidity titration and tumor recognition. A. Bulk CTL cultures stained with CEA tetramer. B. Titration of CTL avidity using cytolytic assay of peptide-pulsed T2 cells at E:T = 10. CTL-DC/CD40L, closed circles; CTL-DC/CD40L/TRICOM, closed triangles. C. Normalization of data shown in B as expressed as percentage of maximal lysis to calculate avidity. D. CTL ability to lyse tumor cells expressing CEA using a standard 4-hour 51Cr release assay. CTL derived from DC/CD40L, lysis of HLA-A2+, CEA+ SW1463 colon cancer cells (closed circles) and HLA2+, CEA− SKMEL24 melanoma cells (open circles); CTL derived from DC/CD40L/TRICOM, lysis of SW1463 (closed triangles) and SKMEL24 (open triangles). E, Tetramer-purified CTL. Ten days after four IVS, tetramer positive CTL were isolated as described in Materials and Methods. Purity of the isolated T cells was analyzed by FACS. Avidity titration at E:T = 0.5. (F), normalization (G) and tumor cell killing assay (H) were performed as above for bulk CTL cultures. n=3, mean ± SD of triplicates. The legends are the same as in bulk CTL cultures. The results are representative of two experiments with two different donors.
