Fig 1.
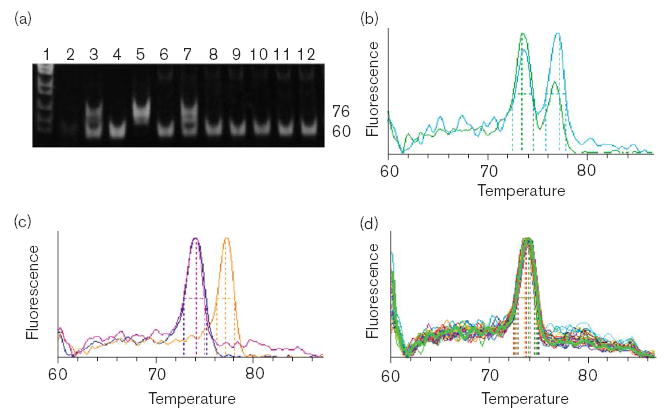
Identification of the g.7,700_7,702dupGAC SNP (encodes p.71Ddup) by (a) electrophoresis or (b–d) real-time detection of PCR products from 3-primer (hF2–44, hF2–45 and hF2–46r) allele-specific amplification. (a) Lane 1: MspI cut pBR322. Lanes 2–7 are control reactions: 2, minus template; 3, synthetic heterozygote composed of reference plasmid + g.7,700_7,702dupGAC plasmid DNA; 4, reference plasmid DNA; 5, g.7,700_7,702dupGAC plasmid DNA; 6, genomic DNA from a reference individual; 7, genomic DNA with added g.7,700_7,702dupGAC plasmid DNA. Lanes 8–12 are from genomic DNA from individual Hispanic-American samples. (b) Melting curve showing control reactions with synthetic heterozygotes; green, mixed plasmid DNA; teal, non-mutant genomic DNA with g.7,700_7,702dupGAC plasmid DNA. (c) Control reactions with simulated homozygotes and a reference homozygote: blue and pink 74°C peaks are from 60-bp products from reference plasmid DNA and genomic DNA, respectively; orange, 77°C peak is from 76-bp product from g.7,700_7,702dupGAC plasmid DNA. (d) Genomic DNA from 30 Hispanic- American individuals showing that the g.7,700_7,702dupGAC is absent.
