Fig. 5.
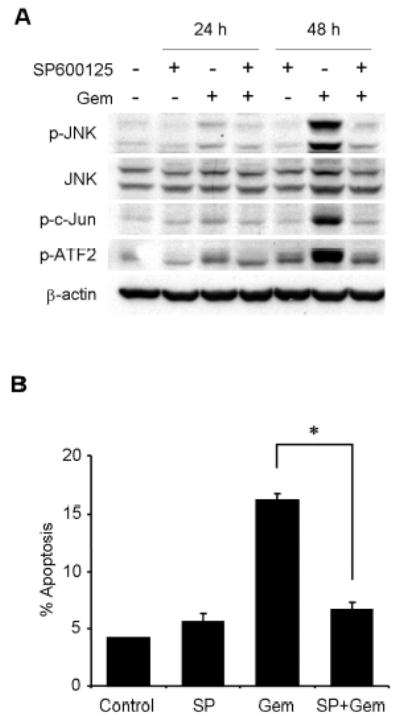
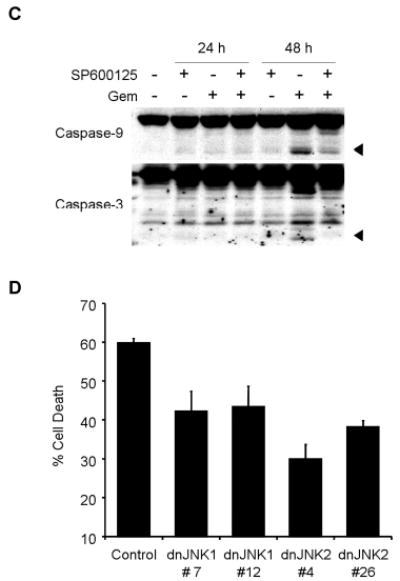
JNK activation has a key role in gemcitabine-induced apoptosis in H1299 cells. (A) H1299 cells were treated with 100 nM gemcitabine (Gem) in the presence or absence of 20 μM SP600125, and harvested at 24 h or 48 h. Whole-cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies as further evidence for blocking JNK activation and apoptosis. (B) H1299 cells were treated with 100 nM gemcitabine (Gem) in the presence or absence of SP600125 (SP) for 48 h, and sub-G1 population, which indicates apoptosis, was determined by FACS analysis. Data represent the means ± SD from three independent experiments. (C) H1299 cells were treated with 100 nM gemcitabine (Gem) in the presence or absence of 20 μM SP600125 for 24 h or 48 h. Whole-cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-caspase-9 and anti-caspase-3 antibodies. Arrowheads represent cleavage proteins. (D) H1299 cells were transfected with plasmid DNA encoding dominant-negative mutant JNK1 or JNK2 and then selected by G418 to obtain stable clones. Stably transfected H1299 clones were treated with 1 μM gemcitabine for 72 h, and then the apoptotic ratios were determined by flow cytometry. Results are the means ± SD from three independent experiments.
