Figure 4.
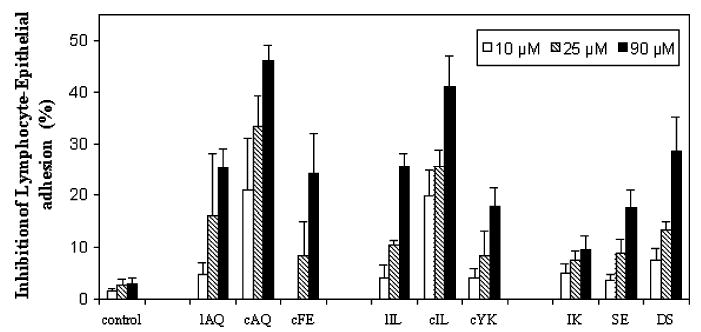
Inhibition of lymphocyte–epithelial adhesion by synthetic peptides derived from CD2 protein. CD58 and CD2 expressed in Caco-2 and Jurkat cells, respectively, were pre-examined. Peptides were added to the confluent Caco-2 monolayer, and then the BCECF-labeled Jurkat cells were added to the mixture. After incubation for 45 min at 37 °C, nonadherent Jurkat cells were removed by washing with PBS and the monolayer-associated Jurkat cells were lysed with a Triton X-100 solution. Soluble lysates were transferred to 96-well plates for reading in a microplate fluorescence analyzer. Values are showed as the percent inhibition of peptide-treated cells and expressed as the mean of three independent experiments.
