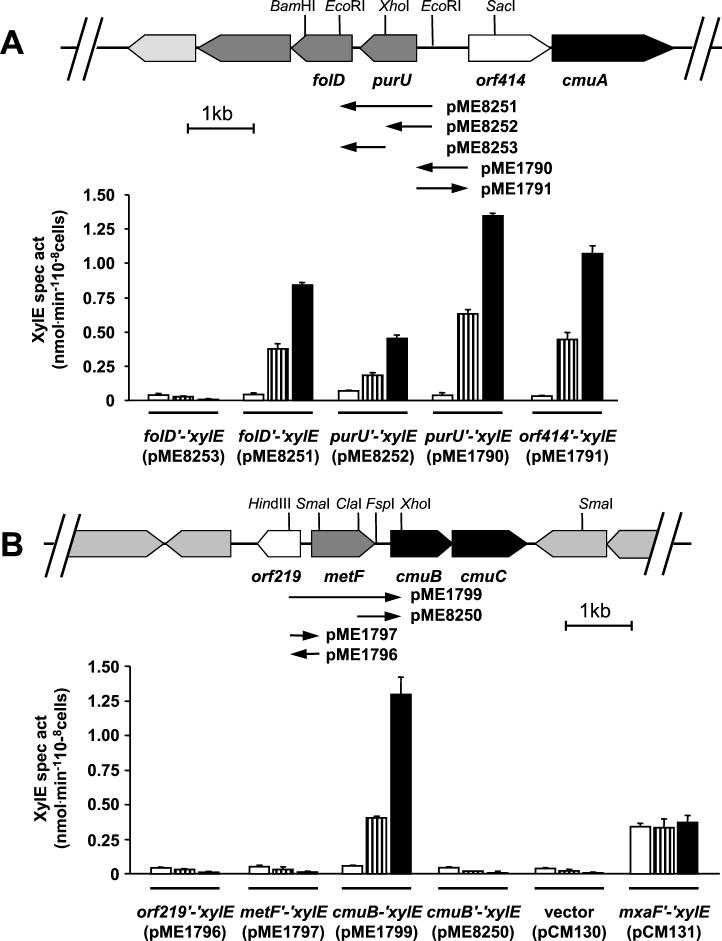
FIG. 2.
Expression of plasmid-borne xylE fusions in M. chloromethanicum CM4. Genetic organization of the gene clusters I (A) and II (B) involved in chloromethane utilization in M. chloromethanicum CM4 (36). Genes encoding methyltransferases are shown in black, genes encoding putative H4folate-dependent enzymes in C1 metabolism are shown in dark gray, vitamin B12 biosynthesis genes are shown in light gray, and genes of unknown function are shown in white. Bar diagrams show catechol dioxygenase activity in transconjugants of wild-type M. chloromethanicum CM4 with different intergenic DNA sequences fused to the promoterless xylE gene of vector pCM130 (18) grown on methanol (□), a mixture of methanol and chloromethane (hashed bars), or chloromethane (▪). Plasmid constructs (see Materials and Methods) are schematically indicated below the sequence, with the orientation of the xylE gene indicated by a black arrowhead.