Figure 3. Sequence alignment of membrane-bound guanylate cyclases.
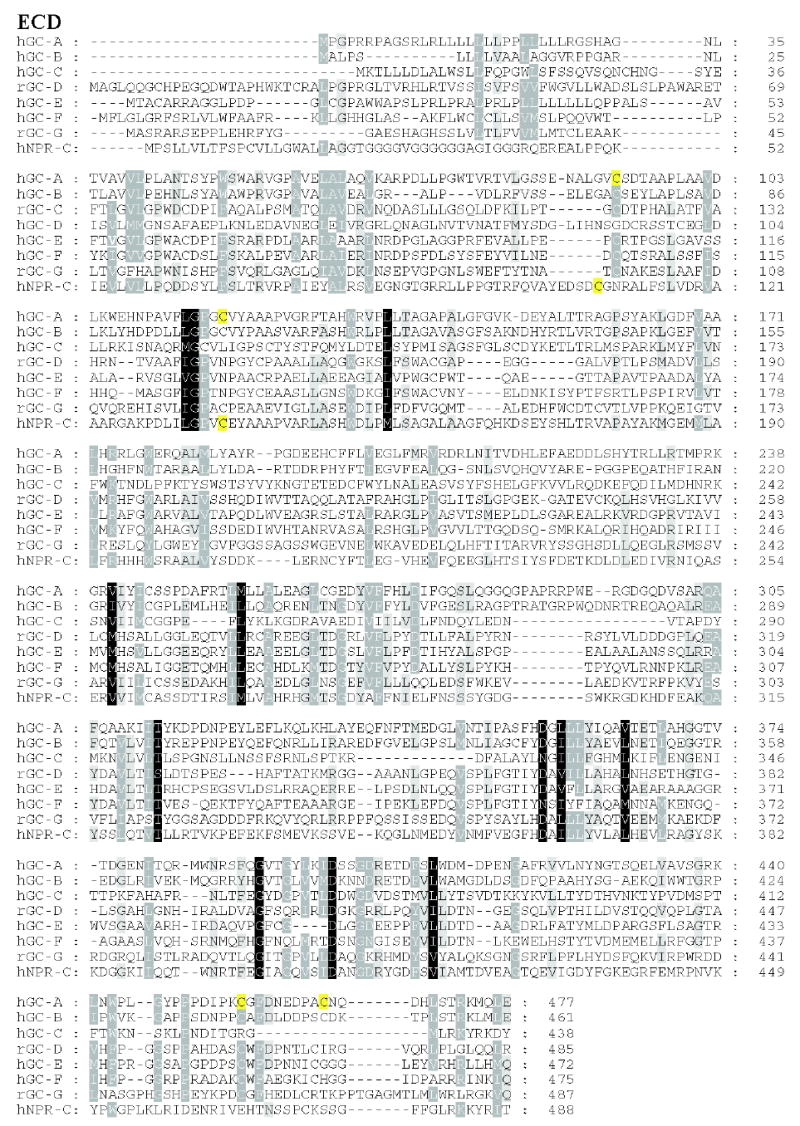
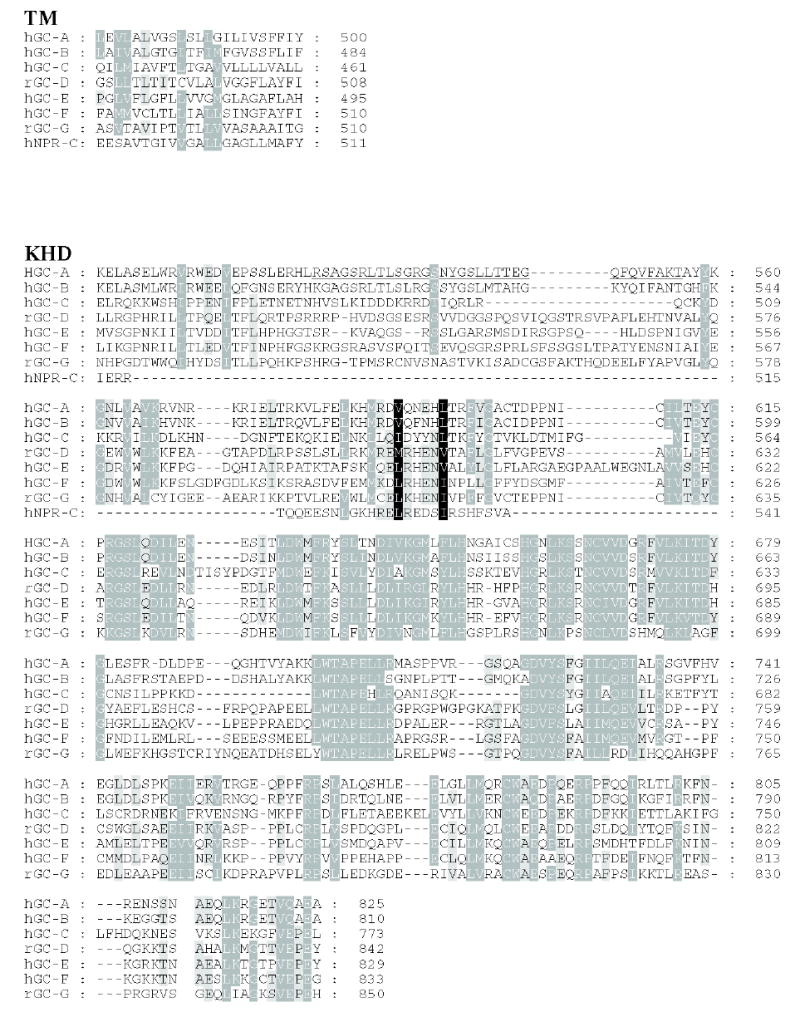
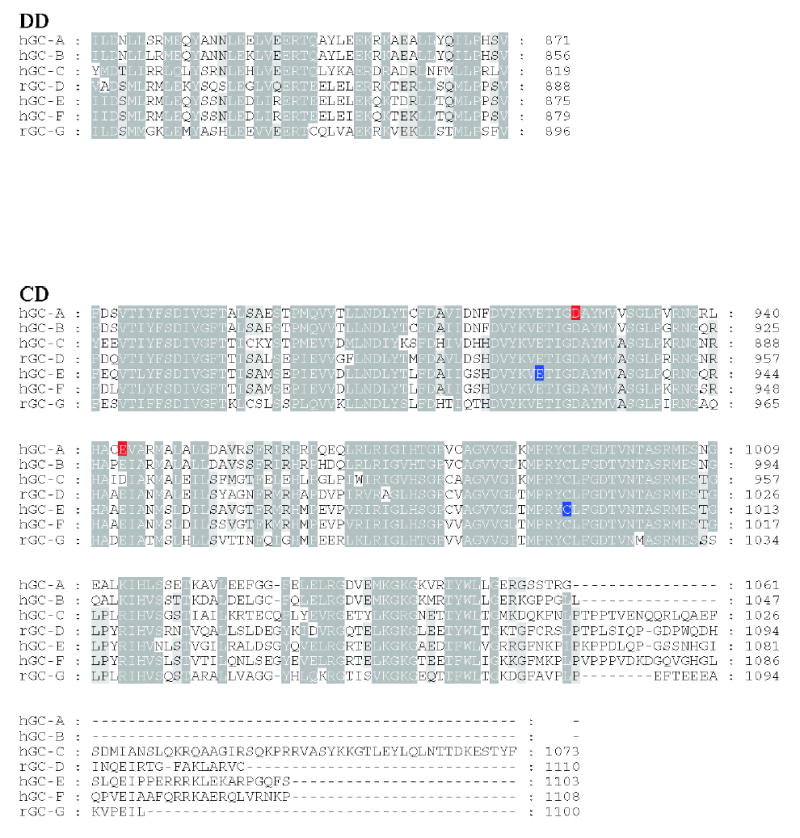
Residues that are 80–100% identical or highly homologous are in white letters on the black background, residues that are 60–80% homologous are in white letters on the gray background and residues that are 40–60% homologous on the gray background. For GC-F, the first 56 amino-acid residues (bovine) is the cleaved signal peptide. The cleavage site is showed in bold font and underlined letter (Margulis et al., 1993). Two residues (marked on the blue background) in the catalytic site when mutated from E925K and C995D are sufficient to alter the nucleotide specificity from GTP to ATP (Tucker et al., 1998). The highly phosphorylated region in GC-A within KHD is underlined. Note that this region is poorly conserved among photoreceptors GC. In red are residues that lead to full inactivation of GC-A (D to A) or hyperactivity (E to A) (Thompson & Garbers, 1995). The sequences were downloaded from the ExPASy Molecular Biology Server (Swiss Protein Data).
