Fig. 2.
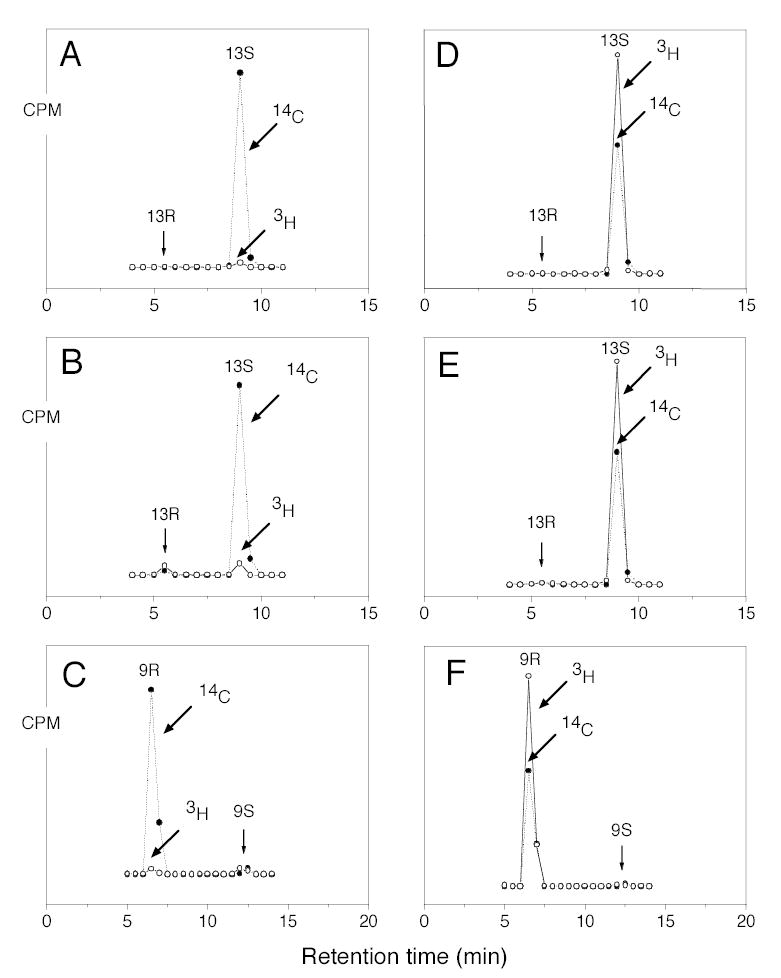
Chiral HPLC analysis of metabolites from incubation of wild-type and mutant soybean LOX-1 with stereospecifically 3H-labeled linoleic acids. A, 13-HODE-Me from incubation of wild-type enzyme with [11S-3H]linoleic acid. B, 13-HODE-Me from incubation of Ala542Gly mutant with [11S-3H]linoleic acid. C, 9-HODE-Me from incubation of Ala542Gly mutant with [11S-3H]linoleic acid. D, 13-HODE-Me from incubation of wild-type enzyme with [11R-3H]-linoleic acid. E, 13-HODE-Me from incubation of Ala542Gly mutant with [11R-3H]linoleic acid. F, 9-HODE-Me from incubation of Ala542Gly mutant with [11R-3H]linoleic acid. Reactions were monitored on a UV spectrophotometer and stopped when 80 % of the substrate had been converted. After reduction with TPP metabolites were converted to their methyl esters with ethereal diazomethane and purified by SP-HPLC prior to chiral HPLC analysis.
