Figure 1.
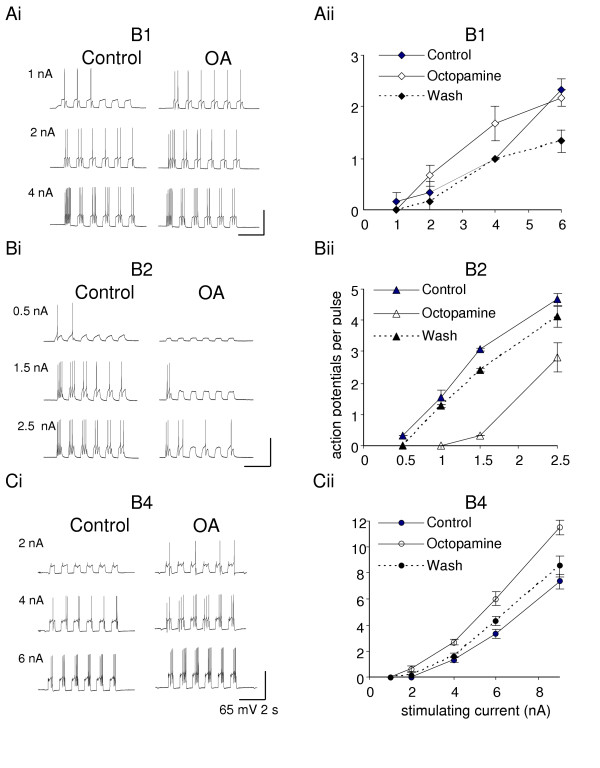
Octopamine (OA, 10 μM) modulates the excitability of the feeding buccal neurons. In the B1 and B4 motoneurons the threshold for action potential generation decreases (A, C), while the B2 motoneuron is less excitable with octopamine in the bath. For the B1 motoneuron the increase of the excitability with octopamine is particularly visible around threshold, while in B4 motoneurons increase of excitability is clear throughout the whole range of the injected current. All control experiments were in Hi-Di saline (to which octopamine was added), and a second electrode was used to inject the constant current pulses to evoke bursts of action potentials. Summary graphs represent dose-response relationship: injected current values (X) versus the mean (± SE) number of action potentials (Y) per 0.5 s depolarizing pulse. N = 6 (Aii), N = 3 (Bii), N = 6 (Cii).
