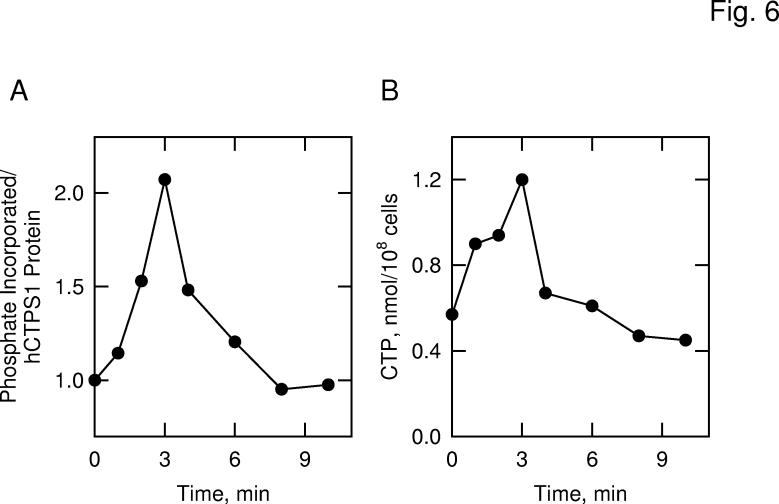
Fig. 6.
Effects of protein kinase A activation on the phosphorylation of human CTP synthetase 1 and on the cellular concentration of CTP in S. cerevisiae. Panel A, cells expressing human CTP synthetase 1 (strain GHY55) were labeled with 32Pi for 3 h in low phosphate YEPA medium. Following the labeling period, glucose was added to a final concentration of 5% to activate the Ras-cAMP pathway and protein kinase A activity. Human CTP synthetase 1 was precipitated from lysates with Ni2+-NTA resin, followed by SDS-PAGE and transfer of proteins to PVDF membrane. The membrane was subjected to phosphorimaging and immunoblot analyses followed by the quantification of the signals using ImageQuant software. Relative phosphorylation was calculated by dividing the signal intensity of 32P-labeled human CTP synthetase 1 by that of enzyme protein. The extent of phosphorylation of human CTP synthetase 1 before glucose addition was set at 1. Panel B, in a separate experiment, the cellular concentration of CTP was measured from unlabeled cells that were activated in the Ras-cAMP pathway. The data are representative of two independent experiments.