Figure 3.
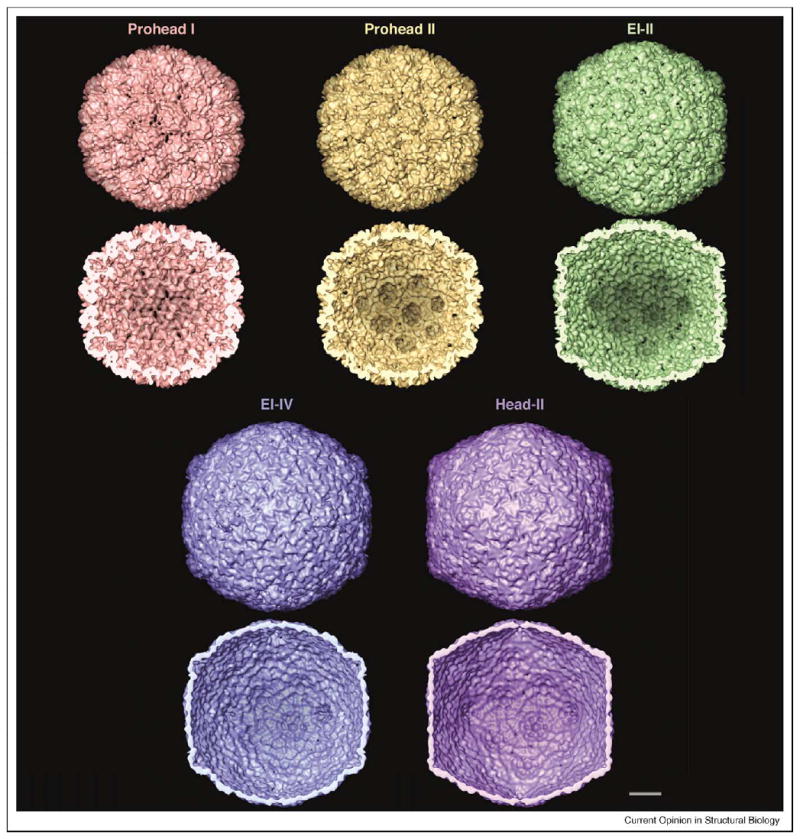
Maturation pathway of the HK97 capsid, visualized in surface renderings (outer surface, upper rows; inner surface, lower rows) at ~14 Å resolution. All images are from cryo-EM reconstructions, except Head II, which is a resolution-limited rendition of the crystal structure [19]. The capsid has icosahedral geometry (T=7 laevo) and is viewed along a twofold axis of symmetry. Prohead I is composed of 420 copies of gp5. In Prohead II, the N-terminal Δ domains have been removed from the inner surface. In acid-induced maturation in vitro, the first transition state, EI-I (not shown), is about 10% bigger than Prohead II [29] and very similar to EI-II [33••] (shown). The main difference between EI-I and EI-II is that EI-II has some covalent cross-links [31•]. The next structural state is a thin-walled spherical particle called the ‘balloon’. Balloons vary in their extents of cross-linking, as in EI-III (variable partial cross-linking) and EI-IV (almost complete cross-linking). The balloon structure is very similar to that of the end-state Head, except for the positions of its pentons, which move ~30 Å outwards in the final transition. Bar = 100 Å .
