Figure 1.
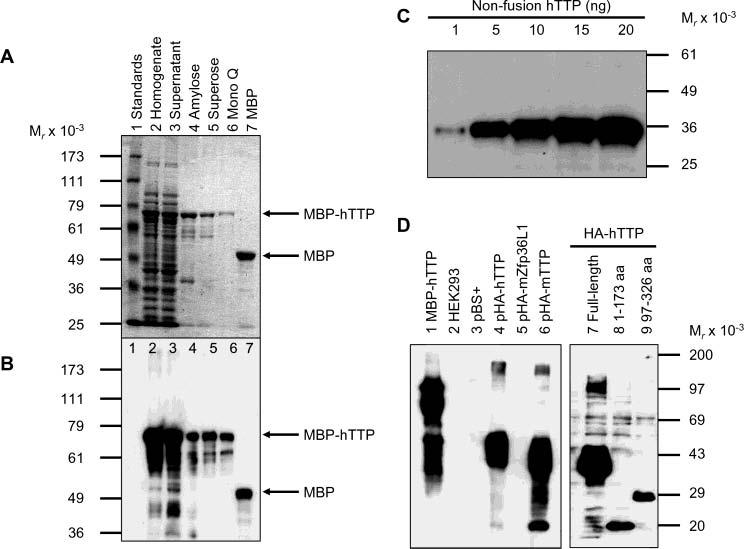
Purification of MBP–hTTP from E. coli and characterization of anti-MBP–hTTP antibodies. (A) Purification of MBP–hTTP stained with Coomassie blue: lane 1, protein size standards; lane 2, homogenate (50 μg of protein); lane 3, supernatant (50 μg); lane 4, amylose resin fraction (5 μg); lane 5, Superose 12 fraction (2 μg); lane 6, Mono Q fraction (1 μg); and lane 7, MBP eluted from the amylose resin column (5 μg). The positions of MBP–hTTP and MBP are indicated. (B) Detection of MBP–hTTP with anti-MBP serum. The samples were identical to those in panel A except that ∼10% of the amount of protein was used in each lane. (C) Detection limit of anti-MBP–hTTP serum by Western blotting. Nonfusion hTTP purified from E. coli as shown in Figure 7A (lane 2) (1, 5, 10, 15, and 20 ng) as indicated was probed with the anti-MBP–hTTP serum (1:10000) for 1 h and with GAR–HRP (1:10000) for 30 min and exposed to X-ray film for 1 min. (D) Characterization of the anti-MBP–hTTP serum by Western blotting. Protein samples were probed with the anti-MBP–hTTP serum (1:10000) for 1 h and with GAR–HRP (1:10000) for 1 h and exposed to X-ray film for 1 min: lane 1, purified MBP–hTTP (50 ng); lane 2, untransfected HEK293 cell extract (50 μg); lane 3, pBS+ transfection extract (50 μg); lane 4, pHA-hTTP transfection extract (50 μg); lane 5, pHA-mZfp36L1/mTIS11b transfection extract (50 μg); lane 6, pHA-mTTP transfection extract (50 μg); lane 7, transfection extract with full-length hTTP (50 μg); lane 8, transfection extract with amino-terminal residues 1–173 of hTTP (50 μg); and lane 9, transfection extract with carboxyl-terminal residues 97–326 of hTTP (50 μg).
