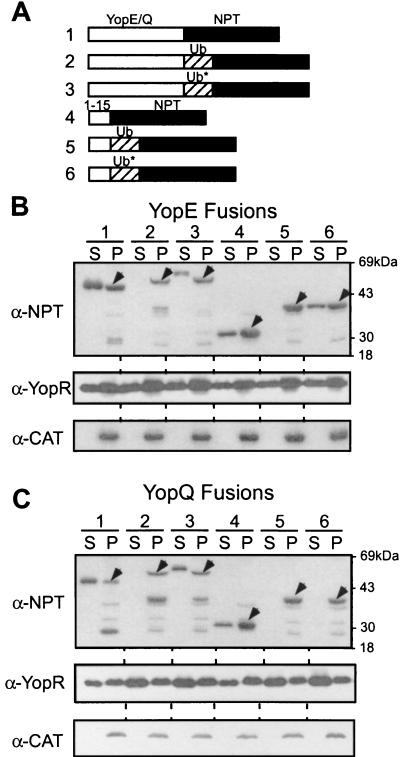
FIG. 1.
Ubiquitin fusions are not secreted by the type III machinery of Y. enterocolitica. (A) The drawing depicts the primary structures of hybrid polypeptides as follows: line 1, YopE1-220-Npt (YopQ1-198-Npt), full-length yop fusion; line 2, YopE1-220-Ub-Npt (YopQ1-198-Ub-Npt), full-length yop ubiquitin fusion; line 3, YopE1-220-UbGly3,13-Npt (YopQ1-198-UbGly3,13-Npt), full-length yop fusion to ubiquitin mutant; line 4, YopE1-15-Npt (YopQ1-15-Npt), yop codons 1 to 15 fused; line 5, YopE1-15-Ub-Npt (YopQ1-15-Ub-Npt), yop codons 1 to 15 fused; line 6, YopE1-15-UbGly3,13-Npt (YopQ1-15-UbGly3,13-Npt), yop codons 1 to 15 fused. Ub represents wild-type ubiquitin, whereas UbGly3,13 carries two mutations that substitute codons 3 (isoleucine) and 13 (isoleucine) with glycine codons, causing destabilization of the folded polypeptide. Npt, neomycin phosphotransferase. (B) Y. enterocolitica strain W22703 (wild type) was transformed with plasmids listed in Table 1, grown in tryptic soy broth supplemented with 5 mM EGTA, and induced for type III secretion by a temperature shift to 37°C. Cultures were centrifuged, and the extracellular medium was separated with the supernatant (S) from the bacterial pellet (P). Proteins were precipitated with TCA, suspended in sample buffer, separated on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and analyzed by immunoblotting with specific antibody (α-Npt, α-YopR, or α-Cat). (C) Y. enterocolitica strain W22703 (wild type) was transformed with plasmids encoding the yopQ hybrids described for panel A and analyzed as described for panel B.