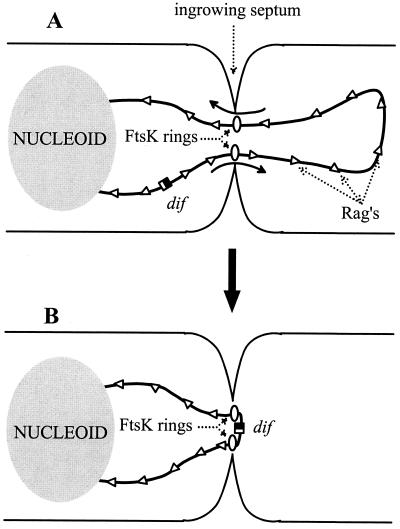
FIG. 5.
How FtsK might eliminate intrusion loops and position dif sites under the septum. (A) A DNA loop extruded from the nucleoid on the left wanders in the cytoplasm of the future sister cell to the right. When the septum is closing, FtsK forms ring structures around the two DNA threads. FtsK mobilizes these threads in the directions (indicated by arrows) dictated by Rags or similar DNA polar elements. (B) When one FtsK ring meets a region polarized in antiorientation (here, the DAZ at the replichore junction near dif), it stops mobilizing DNA; the other ring keeps acting, so that the size of the loop is gradually reduced. When the second ring meets the DAZ, dif is located under the septum and the loop is eliminated.