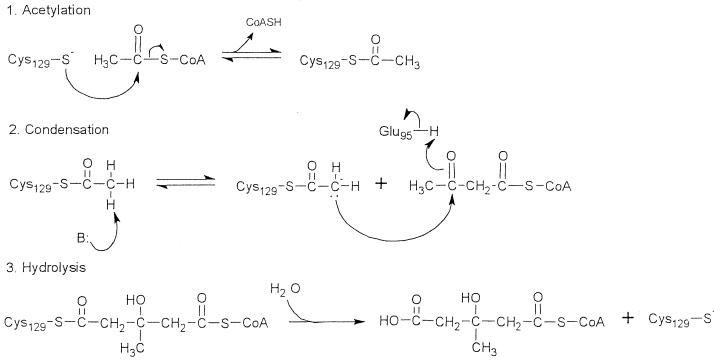
FIG. 5.
Proposed mechanism for catalysis of the HMG-CoA synthase reaction. Active site residues of the avian mitochondrial enzyme include Glu95, Cys129, and His264. During the acetylation step, Cys129 attacks the carbonyl group of acetyl-CoA, forming an acetyl-S-intermediate (17). After the addition and condensation of acetoacetyl-CoA, HMG-CoA is released by hydrolysis. Glu95 acts as the general acid in the condensation step (8), and His264 anchors binding of acetoacetyl-CoA (16).