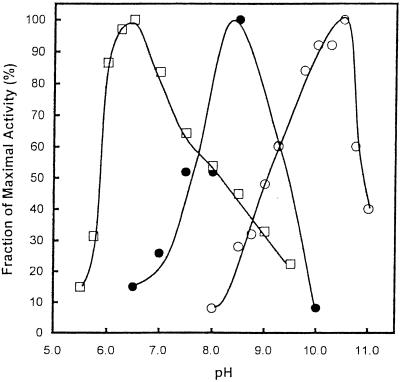
FIG. 6.
Coupled conversion of acetyl-CoA to mevalonate catalyzed by E. faecalis acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase/HMG-CoA reductase and HMG-CoA synthase. Shown is the effect of hydrogen ion concentration on the conversion of acetyl-CoA to acetoacetyl-CoA (○), of HMG-CoA to mevalonate (□), and of acetyl-CoA to mevalonate (•). All assays employed 50 mM sodium acetate, 50 mM glycine, 50 mM Tris, and 50 mM 2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid at the indicated pH. Assays of acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase and HMG-CoA reductase activity were conducted essentially as previously described (11), but under the above conditions. For the conversion of acetyl-CoA to mevalonate, the additions were: 1 mM acetyl-CoA, 0.4 mM NADPH, 9 nM E. faecalis acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase/HMG-CoA reductase subunit, and 16 nM E. faecalis HMG-CoA synthase.